Abstract
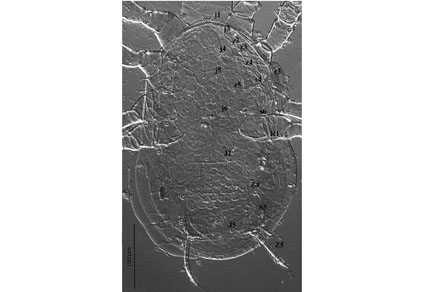
Phytoseiid mites play a key role in regulating mites and small phytophagous insects and are often employed in agricultural systems for biological pest control. Studying the phytoseiid fauna in different ecoregions facilitates the discovery of new biological control agents adapted to local conditions, contributing both to the improvement of control programs and conservation of the natural vegetation that hosts this fauna. The aim of this work was to carry out a survey of phytoseiids and describe a new species for the family in areas of the Caatinga biome in the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Sampling was carried out in three areas in the municipalities of Bonito, Caruaru and São Caetano, including a total of 47 botanical species. A total of 1,044 adult specimens (females and males) were collected, belonging to 37 species from 17 genera. Amblyseiinae was the subfamily with the highest number of species reported (26), followed by Typhlodrominae (6) and Phytoseiinae (5). The species Amblyseius operculatus De Leon, Euseius mesembrinus (Dean), Iphiseiodes zuluagai Denmark & Muma, Phytoseius woodburyi De Leon and Galendromus (Mugidromus) agreste Silva, Gondim Jr. & Demite were the most abundant. The highest phytoseiid species richness was observed on Guazuma ulmifolia (Malvaceae), Piper sp. (Piperaceae), Swartzia sp. (Fabaceae), and Trema micrantha (Cannabaceae). The diversity of phytoseiids in the Caatinga biome is high, and their association with native plants may indicate that these plants may serve as important reservoirs. This information can be used to improve future integrated pest management programs. A new species, Metaseiulus (Metaseiulus) fungicolus sp. nov., is described and illustrated, based on adult females.
References
- Abou-Setta, M.M., Childers, C.C., Denmark, H.A. & Browning, H.W. (1991) Comparative morphology and reproductive compatibility between populations of Euseius mesembrinus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Florida and Texas. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 10, 213–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01198651
- Abo-Shnaf, R.I., Sánchez, L.& Moraes, G.J. de (2016) Plant inhabiting Gamasina mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) from the Dominican Republic, with descriptions of four new species of Lasioseius (Blattisociidae) and complementary descriptions of other species. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 21, 607–646. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.21.5.5
- Akyazi, R., Ueckermann, E.A. & Soysal, M. (2016) The new distribution of Amblyseius herbicolus in Turkey (Parasitiformes, Phytoseiidae) with a key of Amblyseius species found in Turkey. Acarologia, 56, 237–244. https://doi.org/10.1051/acarologia/20162241
- Andrade-Lima, D. (1982) Present day forest refuges in Northeastern Brazil. In: Prance, G.T. (Ed.), Biological Diversification in the Tropics. Columbia University Press, New York, New York, pp. 245–254.
- Antongiovanni, M., Venticinque, E.M. & Fonseca, C.R. (2018) Fragmentation patterns of the Caatinga drylands. Landscape Ecology, 33, 1353–1367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-018-0672-6
- APAC [Agência Pernambucana de Águas, Clima] (2023) Climatologia por município. Recife, APAC. Available from: https://www.apac.pe.gov.br/193-climatologia/521-climatologia-por- municipio (accessed 2 January 2023)
- Aponte, O. & McMurtry, J.A. (1993) Phytoseiid mites of Venezuela (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 19 (2), 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647959308683974
- Araújo, I.F. & Rodrigues, J.K. (2023) Revisão dos ácaros Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) associados ao bioma Caatinga: compilação de dados, checklist. Journal of Neotropical Biology, 20 (2), 54–70. https://doi.org/10.5216/rbn.v20i2.75417
- Barbosa, M.F.C., Demite, P.R., Lofego, A.C., Vasconcelos, G.J. & Moraes, G.J. de (2021) Further records of phytoseiid (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) species for Brazil. Entomological Communications, 3 (ec03048), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.37486/2675-1305.ec03048
- Baldo, F.B., Mineiro, J.L.D.C. & Raga, A. (2018) Diversity and population dynamics of mites in peach and plum trees (Rosaceae) in the Southwest State of São Paulo, Brazil. International Journal of Acarology, 44, 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2018.1436589
- Brito, E.A.S., Castro, I.S., Noronha, A.C.S. & Ferla, N.J. (2024) Mites associated with açaí palm trees (Euterpe oleracea: Arecaceae) in native and cultivated areas of the state of Pará (Eastern Amazon, Brazil). Experimental and Applied Acarology, 93, 229–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-024-00925-4
- Buosi, R., Feres, R.J.F., Oliveira, A.R.., Lofego, A.C. & Hernandes, F.A. (2006) Ácaros plantícolas (Acari) da “Estação Ecológica de Paulo de Faria”, Estado de São Paulo, Brasil. Biota Neotropica, 6, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1676-06032006000100009
- Carvalho, A.N., Argolo, P.S., Ferragut, F., Moraes, G.J. de, Beaulieu, F., Navia, D.& Oliveira, A.R. (2019) New morphological data for Leonseius regularis (De Leon) (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and a description of a new species of the genus from Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 24, 2119–2132. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.24.11.7
- Castro, T.M.M.G. & Moraes, G.J. de (2007) Mite diversity on plants of different families found in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Neotropical Entomology, 36, 774–782. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2007000500020
- Castro, T.M.M.G & Moraes, G.J. de (2010) Diversity of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) in the Atlantic Forest of São Paulo. Systematics and Biodiversity, 8, 301–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772001003801375
- Castro, I.S., Azevedo, A.O., Vinhas, N.A.N., Schlemer, S.M, Wurlitzer, W.B., Freitas, E. M., Heiden, G. & Ferla, N.J. (2024) Phytoseiid mites associated with Asteraceae plants in the Pampa biome with description of two new species. International Journal of Acarology, 50, 570–586. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2024.2387717
- Cavalcante, A.C.C., Demite, P.R., Lofego, A.C. &. Hernandes, F.A. (2021) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) from the Atlantic Forest in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, with complementary description of Amblyseius impeltatus Denmark & Muma. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia, 61, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.11606/1807-0205/2021.61.98
- Cavalcante, A.C.C., Demite, P.R., Amaral, F.S.R., Lofego, A.C., & Moraes, G.J. de (2017) Complementary description of Neoseiulus tunus (De Leon) (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) and observation on its reproductive strategy. Acarologia, 57, 591–599. https://doi.org/10.24349/acarologia/20174178
- Chant, D.A. (1959) Phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Part I. Bionomics of seven species in southeastern England. Part II. A taxonomic review of the family Phytoseiidae, com descriptions of thirty-eight new species. Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 91, 5–166. https://doi.org/10.4039/entm9112fv
- Chant, D.A. & Baker, E.W. (1965) The Phytoseiidae (Acarina) of Central America. The Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 97, 3–56. https://doi.org/10.4039/entm9741fv
- Chant, D.A. & Yoshida-Shaul, E. (1983) A world review of five similar species groups in the genus Typhlodromus Scheuten. Part II. The conspicuus, cornus groups (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 61, 1041–1057. https://doi.org/10.1139/z83-138
- Chant, D.A. & Yoshida-Shaul, E. (1984) A world review of the occidentalis species group in the genus Typhlodromus Scheuten (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 62, 1860–1871. https://doi.org/10.1139/z84-272
- Chant, D.A. & Yoshida-Shaul, E. (1992) Adult idiosomal setal patterns in the family Phytoseiidae (Acari: Gamasina). International Journal of Acarology, 18, 177–193. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647959208683949
- Chant, D. & McMurtry, J.A. (2003a) A review of the subfamily Amblyseiinae Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Part I. Neoseiulini new tribe. International Journal of Acarology, 29, 3–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950308684319
- Chant, D. & McMurtry, J.A. (2003b) A review of the subfamily Amblyseiinae (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Part II. The tribe Kampimodromini. International Journal of Acarology, 29, 179–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950308684331
- Chant, D.A. & McMurtry, J.A. (2004) A review of the subfamily Amblyseiinae Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Part IV. Tribe Amblyseiini Wainstein, subtribe Arrenoseiina Chant & McMurtry. International Journal of Acarology, 30, 291–312. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950408684399
- Chant, D.A. & McMurtry, J.A. (2005) A review of the subfamily Amblyseiinae Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Part VI. The tribe Euseiini n. tribe, subtribes Typhlodromalina n. subtribe, Euseiina n. subtribe, and Ricoseiina n. subtribe. International Journal of Acarology, 31, 187–224. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950508684424
- Chant, D.A. & McMurtry, J.A. (2007) Illustrated Keys, Diagnoses for the Genera, Subgenera of the Phytoseiidae of the World (Acari: Mesostigmata). Indira Publishing House, West Bloomfield, Michigan, 220 pp.
- Chant, D.A. & Yoshida-Shaul, E. (1991) Adult ventral setal patterns in the family Phytoseiidae (Acari: Gamasina). International Journal of Acarology, 17, 187–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647959108683906
- Chant, D.A., Hansell, R.I.C, Rowell, H.J. & Yoshida-Shaul, E. (1978) A study of the family Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata) using the methods of numerical taxonomy. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 56, 1330–1347. https://doi.org/10.1139/z78-185
- Chaudhri, W.M. (1967) Description of a new mite species of Amblyseius (sub-genus Ptenoseius) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) from Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 4, 266–268.
- Chaudhri, W.M. (1968) Six new species of mites of the genus Amblyseius (Phytoseiidae) from Pakistan. Acarologia, 10, 550–562.
- Climate-data.org. (2022) Clima: Bonito. Available from: https://pt.climate-data.org/america-do-sul/brasil/pernambuco/ bonito-43104/ (accessed 4 October 2022)
- Conceição, E.M., Demite, P.R., Rezende, J.M., Carniello, M.A. & Lofego, A.C. (2021) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Parasitiformes: Mesostigmata) inhabiting native plants from three biomes in Mato Grosso State, Brasil, with description of a new species. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 26, 2268–2286. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.26.12.6
- Daneshvar, H. & Denmark, H.A. (1982) Phytoseiids of Iran (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 8, 3–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958208683272
- DCA [Departamento de Ciências Atmosféricas] (2022) Precipitação mensal - Estado de Pernambuco. Available from: http://app.dca.ufcg.edu.br/EST-PRINCIPAL (accessed 9 February 2023)
- Dean, H.A. (1957) Predators of Oligonychus pratensis (Banks), Tetranychidae. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 50, 164–165. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/50.2.164
- De Leon, D. (1958) Four new Typhlodromus from southern Florida (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Florida Entomologist, 41, 73–76. https://doi.org/10.2307/3492363
- De Leon, D. (1959) Seven new Typhlodromus from Mexico com collection notes on three other species (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). The Florida Entomologist, 42, 113–121. https://doi.org/10.2307/3492606
- De Leon, D. (1961) Eight new Amblyseius from Mexico with collection notes on two other species (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). The Florida Entomologist, 44, 85–91. https://doi.org/10.2307/3492318
- De Leon, D. (1965a) Phytoseiid mites from Porto Rico com descriptions of new species (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Florida Entomologist, 48, 121–131. https://doi.org/10.2307/3493102
- De Leon, D. (1965b) Ten new species of Phytoseius (Pennaseius) from Mexico, Trinidad, and British Guiana with a key to species (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Entomological News, 76, 11–21.
- De Leon, D. (1966) Phytoseiidae of British Guyana with keys to species. In: Geijakes, D.C. & Wagennar Hummelinck, P. (Eds.), Studies on the Fauna of Suriname and other Guyanas. Vol.8. Guyanas, Foundation for Scientific Research, pp. 81–102.
- De Leon, D. (1967) Some mites of the Caribbean Area. Part I. Acarina on plants in Trinidad, West Indies. Allen Press, Lawrence, Kansas, 66 pp.
- Demite, P.R., Feres, R.J.F., Lofego, A.C. & Oliveira, A.R. (2009) Plant inhabiting mites (Acari) from the Cerrado biome of Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Zootaxa, 2061 (1), 45–60. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2061.1.3
- Demite, P.R., Lofego, A.C. & Feres, R.J.F. (2011) Phytoseiidae (Acari) in forest fragments in the State of São Paulo, Brasil. Zootaxa, 3086 (1), 31–56. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3086.1.2
- Demite, P.R., Lofego, A.C. &. Feres, R.J.F. (2013) Mite (Acari; Arachnida) diversity of two native plants in fragments of a semideciduous seasonal forest in Brazil. Systematics and Biodiversity, 11, 141–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2013.806368
- Demite, P.R., Cavalcante, A.C., Dias, M.A. & Lofego, A.C. (2016) A new species and redescription of two species of Euseius Wainstein (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Cerrado biome areas in Brazil. International Journal of Acarology, 42, 334–340. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2016.1197311
- Demite, P.R., Dias, M.A., Cavalcante, A.C.C., Ramos, M.V.V. & Lofego, A.C. (2017) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) associated with Cerrado biome plants in Brazil, with description of a new species. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 22, 2141–2177. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.22.12.9
- Demite, P.R., Rezende, J.M., Lofego, A.C., Amaral, F.S.R., Barreto, M.R. & Moraes, G.J. de (2021) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) from Mato Grosso State, Central-Western Brazil. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências, 93 (3), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202120200729
- Demite, P.R., Moraes, G.J. de, McMurtry, J.A., Denmark, H.A. &. Castilho, R.C. (2025a) Phytoseiidae Database. Available from: www.lea.esalq.usp.br/phytoseiidae (accessed 16 August 2025)
- Demite, P.R., Oliveira, F.A., Gomes, M..S., Moraes, G.J. de, Holtz, A. M., & Moreira, G.F. (2025b) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) on wild and cultivated plants in Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia, 65 (e202565016), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.11606/1807-0205/2025.65.016
- Denmark, H.A. (1966) Revision of the genus Phytoseius Ribaga, 1904 (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Florida Department of Agriculture Bulletin, 6, 1–105.
- Denmark, H.A. & Muma, M.H. (1970) Some phytoseiid mites of Paraguay (Phytoseiidae: Acarina). Florida Entomologist, 53, 219–227. https://doi.org/10.2307/3493192
- Denmark, H.A. & Muma, M.H. (1972) Some Phytoseiidae of Colombia (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Florida Entomologist, 55, 19–29. https://doi.org/10.2307/3493637
- Denmark, H.A. & Muma, M.H. (1973) Phytoseiid mites of Brasil (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Revista Brasileira de Biologia, 33, 235–276.
- Denmark, H.A. & Muma, M.H. (1989) A revision of the genus Amblyseius Berlese, 1914 (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Occasional Papers of the Florida State Collection of Arthropods, 4, 1–149.
- Diehl, M., Ferla, N. J. & Johann, L. (2012) Plantas associadas à videiras: uma estratégia para o controle biológico no Rio Grande do Sul. Arquivos do Instituto Biológico, 79, 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1808-16572012000400015
- Duarte, M.E., Demite, P.R., Mendonça, R.S., Michereff-Filho, M., Mesquita, M.L.S.C., Peixoto, J.R. & Navia, D. (2021) Phytoseiidae mites associated with native and cultivated solanaceous in Central-West Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 26, 2358–2384. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.26.12.13
- Ehara, S. (1967) Phytoseiid mites from Okinawa Island (Acarina: Mesotigmata). Mushi, 40, 67–82.
- El-Banhawy, E.M. (1975) New Amblyseius mite from Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Biologia, 35, 549–552.
- El-Banhawy, E.M. (1978) Description of some unknown phytoseiid mites from Brazil (Mestostigmata: Phytoseiidae). Acarologia, 20, 477–484.
- El-Banhawy, E.M. (1984) Description of some phytoseiid mites from Brasil (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Acarologia, 25, 125–144.
- Feres, R.J.F. & Moraes, G.J. de (1998) Phytoseiidae mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from woody areas in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 3, 125–132. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.3.1.20
- Ferla, N.J. & Moraes, G.J. de (1998) Ácaros predadores em pomares de maçã no Rio Grande do Sul. Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil, 27 (4), 649–654. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0301-80591998000400019
- Ferla, N.J. & Moraes, G.J. de (2002a) Ácaros (Arachnida, Acari) da seringueira (Hevea brasiliensis Muell.Arg.) no Estado do Mato Grosso, Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 19 (3), 867–888. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81752002000300025
- Ferla, N.J. & Moraes, G.J. de (2002b) Ácaros predadores (Acari) em plantas nativas, cultivadas do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 19, 1011–1031. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81752002000400006
- Ferla, N.J., Marchetti, M.M. & Siebert, J.C. (2005) Acarofauna (Acari) de erva-mate (Ilex paraguariensis St. Hil.: Aqüilofoliaceae) no estado do Rio Grande do Sul. Biociências, 13 (2), 133–142. [onlin]
- Ferla, N.J., Johann, L. Klock, C., Majolo, F. & Botton, M. (2011) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from vineyards in Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. Zootaxa, 2976 (1), 15–31. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2976.1.2
- Ferragut, F. & Navia, D. (2017) Phytoseiid Mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) of the Azores Islands. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 22, 1585–1621. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.22.10.4
- Ferragut, F. & Navia, D. (2022) The tribes Kampimodromini Kolodochka, Typhlodromipsini Chant & McMurtry (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) in the Serra do Espinhaço, Brasil, com a key to the Brasilian species of Typhlodromips De Leon. Acarologia, 62, 1217–1253. https://doi.org/10.24349/mi5x-xnne
- Ferragut, F. & Navia, D. (2024a) Phytoseius Ribaga (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) in the Brazilian Espinhaço Range: seven new species, renaming of the plumifer species group, and a critical review of its taxonomic characters. Zootaxa, 5493 (3), 201–245. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5493.3.1
- Ferragut, F. & Navia, D. (2024b) The subfamily Typhlodrominae Wainstein (Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) in the Serra do Espinhaço, Brazil, with the description of a new genus and two new species. International Journal of Acarology, 50, 87–108. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2023.2290665
- Ferragut, F., Moraes, G.J. de & Navia, D. (2011) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) of the Dominican Republic, with a re-definition of the genus Typhloseiopsis De Leon. Zootaxa, 2997 (1), 37–53. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2997.1.3
- Fiaboe, K.K.M., Gondim Jr, M.G.C., Moraes, G.J. de, Ogol, C.K.P.O., Knapp, M. (2007) Surveys for natural enemies of the tomato red spider mite Tetranychus evansi (Acari: Tetranychidae) in northeastern and southeastern Brazil. Zootaxa, 1395 (1), 33–58. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1395.1.2
- Gonçalves, D., Silva, G.L. & Ferla, N.J. (2013) Phytoseiid mites (Acari) associated with yerba mate in southern Brazil, with description of a new species. Zootaxa, 3746 (2), 357–371. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3746.2.6
- Gonçalves, D., Cunha, U.S., Bampi, P.M., Moraes, G.J. de & Ferla, N.J. (2015) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Mesostigmata) from Araucaria Forest of the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, with new records and descriptions of four new species. Zootaxa, 4032 (5), 569–581. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4032.5.6
- Gondim, Jr., M.G.C. & Moraes, G.J. de (2001) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) associated with palm trees (Arecaceae) in Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 6, 65–94. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.6.1.11
- Guanilo, A.D. & Martínez, N. (2007) Predadores asociados a Panonychus citri McGregor (Acari: Tetranychidae) en la costa central del Perú. Ecología Aplicada, 6, 119–129. https://doi.org/10.21704/rea.v6i1-2.348
- Guanilo, A.D., Moraes, G.J. de & Knapp, M. (2008a) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) of the subfamily Amblyseiinae Muma from Peru, with descriptions of four new species. Zootaxa, 1880 (1), 1–47. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1880.1.1
- Guanilo, A.D., Moraes, G.J. de, Toledo, S. & Knapp, M. (2008b) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Argentina, with description of a new species. Zootaxa, 1884 (1), 1–35. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1884.1.1
- Gupta, S.K. (2003) A monograph on plant inhabiting predatory mites of India. Part II: Order: Mesostigmata. Memoirs of the Zoological Survey of India, 20, 1–185.
- Hirschmann, W. (1962) Gangystematik der Parasitiformes. Gamasiden. Rückenhaarbestimmungstafeln von 260 Typhlodromus Arten der Erde Acarologie. Schriftenreihe für Vergleichende Milbenkunde, 5, 1–56.
- Horn, T.B., Johann, L. & Ferla, N.J. (2011) Ecological interactions between phytophagous and predaceous mites in citrus agroecosystems in Taquari Valley, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 16, 133–144. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.16.2.2
- Hoy, M.A. (2011) Agricultural Acarology. Introduction to Integrated Mite Management. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 410 pp.
- Kabíček, J. (2003) Broad leaf trees as reservoirs for phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Plant Protection Science, 39, 65–69. https://doi.org/10.17221/3828-PPS
- Karban, R., English-Loeb, G., Walker, M.A. & Thaler, J. (1995) Abundance of phytoseiid mites on Vitis species: effects of leaf hairs, domatia, prey abundance and plant phylogeny. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 19, 189–197. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00130822
- Karg, W. (1983) Systematische untersuchung der Gattungen und Untergattungen der Raubmilbenfamilie Phytoseiidae Berlese, 1916, mit der beschreibung von 8 neuen Arten. Mitteilungen Zoologisches Museum in Berlin, 59, 293–328. https://doi.org/10.1002/mmnz.4830590203
- Klock, C.L., Botton, M. & Ferla, N.J. (2011) Mitefauna (Arachnida: Acari) associated to grapevine, Vitis vinifera L. (Vitaceae), in the municipalities of Bento Gonçalves and Candiota, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Check List, 7 (4), 522–536. https://doi.org/10.15560/7.4.522
- Kreiter, S. & Moraes, G.J. de (1997) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Guadeloupe and Martinique. Florida Entomologist, 80, 376–382. https://doi.org/10.2307/3495770
- Kreiter, S., Tixier, M.-S., Croft, B.A., Auger, P. & Barret, D. (2002) Plants and leaf characteristics influencing the predaceous mite Kampimodromus aberrans (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in habitats surrounding vineyards. Environmental Entomology, 31, 648–660. https://doi.org/10.1603/0046-225X-31.4.648
- Kreiter, S., Zriki, G., Ryckewaert, P., Pancarte, C., Douin, M.& Tixier, M-S. (2018) Phytoseiid mites of Martinique, with redescription of four species and new records (Acari: Mesostigmata). Acarologia, 58, 366–407. https://doi.org/10.24349/acarologia/20184248
- Kreiter, S., Payet, R.M., Douin, M., Fontaine, O., Fillâtre, J.& Le Bellec, F. (2020) Phytoseiidae of La Réunion Island (Acari: Mesostigmata): three new species and two males described, new synonymies, and new records. Acarologia, 60, 111–195. https://doi.org/10.24349/acarologia/20204361
- Johann, L., Horn, T.B., Carvalho, G.S. & Ferla, N.J. (2014) Diversity of mites (Acari) in vineyard agroecosystems (Vitis vinifera) in two viticultural regions of Rio Grande do Sul state, Brazil. Acarologia, 54, 137–154. https://doi.org/10.1051/acarologia/20142122
- Lindquist, E.E. (1994) Some observations on the chaetotaxy of the caudal body region of gamasine mites (Acari, Mesostigmata), com a modified notation for some ventrolateral body Setas. Acarologia, 35, 323–326.
- Lindquist, E.E. & Evans, G.O. (1965) Taxonomic concepts in the Ascidae, with a modified setal nomenclature for the idiosoma of the Gamasina (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 97, 5–66. https://doi.org/10.4039/entm9747fv
- Lofego, A.C. & Moraes, G.J. de (2006) Ácaros (Acari) Associados a Mirtáceas (Myrtaceae) em Áreas de Cerrado no Estado de São Paulo com Análise Faunística das Famílias Phytoseiidae, Tarsonemidae. Neotropical Entomology, 35, 731–746. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2006000600003
- Lofego, A.C., Moraes, G.J. de & McMurtry, J.A. (2000) Three new species of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Brazil. Anais da Sociedade Entomológica do Brasil, 29, 461–467. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0301-80592000000300008
- Lofego, A.C., Moraes, G.J. de & Castro, L.A.S. (2004) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) on Myrtaceae in the State of São Paulo, Brazil. Zootaxa, 516 (1), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.516.1.1
- Lofego, A.C., Rezende, J.M., Demite, P.R. & Feres, R.J.F. (2017) Mite fauna associated with Cecropia pachystachya Trec. (Urticaceae) the importance of the plant as reservoir and dissemination means for predatory mites. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 22, 1780–1794. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.22.10.16
- Lofego, A.C., Barbosa, M.F.C., Demite, P.R. & Moraes, G.J. de (2024) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) of the subfamily Amblyseiinae from Brazil. Zootaxa, 5439 (1), 1–306. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5439.1.1
- Lofego, A.C., Demite, P.R., Kishimoto, R.G. & Moraes, G.J. de (2009) Phytoseiid mites on grasses in Brazil (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 2240 (1), 41–59. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2240.1.3
- Lopes, P.C., McMurtry, J.A. & Moraes, G.J. de (2015) Definition of the concordis species group of the genus Euseius (Acari: Phytoseiidae), com a morphological reassessment of the species included. Zootaxa, 4048 (2), 174–190. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4048.2.2
- Lorenzato, D. (1987) Biological control of phytophagous mites in apple orchards in Farroupilha, RS. Agronomia Sulriograndense, 23 (2), 167–183.
- Loughner, R., Goldman, K., Loeb, G. & Nyrop, J. (2008) Influence of leaf trichomes on predatory mite (Typhlodromus pyri) abundance in grape varieties. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 45, 111–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9183-5
- Ma, M., Zhang, K., Fan, Q.-H. & Zhang, Z.-Q. (2024) Description of ontogenetic changes in the morphology of Amblyseius herbicolus (Chant, 1959) and Amblyseius lentiginosus Denmark & Schicha, 1974 (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Zootaxa, 5485 (1), 7–37. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5485.1.4
- MMA (Ministério do Meio Ambiente). Caatinga. 2024) Available from: https://www.gov.br/mma/pt-br/assuntos/ecossistemas/biomas/caatinga (accessed 4 January 2024)
- MapBiomas. (2022) Destaques do mapeamento anual da cobertura, uso da terra no Brasil de 1985 a 2021. Available from: https://brasil.mapbiomas.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2023/10/MapBiomas_Caatinga_2022_10.10.pdf (accessed 24 March 2024)
- Marchetti, M.M. & Ferla, N.J. (2011) Diversidade, flutuação populacional de ácaros (Acari) em amora-preta (Rubus fruticosus, Rosaceae) no estado do Rio Grande do Sul, Brasil. Iheringia. Série Zoologia, 101 (1–2), 43–48. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0073-47212011000100005
- Matthysse, J.G. & Denmark, H.A. (1981) Some phytoseiids of Nigeria (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Florida Entomologist, 64 (2), 340–357. https://doi.org/10.2307/3494585
- McMurtry, J.A. & Moraes, G.J. de (1989) Some phytoseiid mites from Peru com descriptions of four new species (Acari: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Entomology, 15 (3), 179–188. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958908683843
- McMurtry, J.A., Moraes, G.J. de & Sourassou, N.F. (2013) Revision of the lifestyles of phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and implications for biological control strategies. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 18 (4), 297–320. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.18.4.1
- Mendes, J.A., Lima, D.B., Monteiro, N.V., Gondim Jr., M.G.C. & Melo, J.W.S. (2021) Phytoseiid mites in cashew trees: diversity and seasonality. International Journal of Entomology, 47(4), 339–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2021.1908423
- Mendonça, A.L., Lofego, A.C., Pott, A., Daud, R.D. & Demite, P.R. (2019) Phytoseiidae (Parasitiformes: Mesostigmata) from the Pantanal, Mato Grosso do Sul State, Brasil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 24 (4), 587–612. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.24.4.6
- Mineiro, J.L. & Raga, A. (2020) Mites associated with Citrus latifolia (Rutaceae) from an orchard at Artur Nogueira municipality, São Paulo state, Brazil. Entomological Communications, 2, ec02014, 1–2. https://doi.org/10.37486/2675-1305.ec02014
- Moraes, G.J. de & Flechtmann, C.H.W. (2008) Manual de Acarologia: Acarologia Básica, Ácaros de Plantas Cultivadas no Brasil. Holos, Ribeirão Preto, 308 pp.
- Moraes, G.J. de & Denmark, H.A. (1999) The genus Proprioseius Chant (Acari: Phytoseiidae), with descriptions of two new species from Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 4, 97–102. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.4.1.14
- Moraes, G.J. de & McMurtry, J.A. (1983) Phytoseiid mites (Acarina) of northeastern Brazil with descriptions of four new species. International Journal of Entomology, 9 (3), 131–148. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958308683326
- Moraes, J.G. & Mesa, N.C. (1988) Mites of the family Phytoseiidae (Acari) in Colombia, com descriptions of three new species. International Journal of Entomology, 14 (2), 71–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958808683790
- Moraes, G.J. de, McMurtry, J.A. & Denmark, H.A. (1986) A Catalog of the Mite Family Phytoseiidae. EMBRAPA-DDT, Brasília, 353pp.
- Moraes, G.J. de, Barbosa, M.F.C & Castro, T.M.M.G. (2013) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) from natural ecosystems in the State of São Paulo, Brasil. Zootaxa, 3700 (3), 301–347. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3700.3.1
- Moraes, G.J. de, Mesa, N.C. & Braun, A. (1991) Some phytoseiid mites of Latin America (Acari: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Entomology, 17 (2), 117–139. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647959108683892
- Moraes, G.J. de, Kreiter, S. & Lofego, A.C. (2000) Plant mites (Acari) of the French Antilles. 3. Phytoseiidae (Gamasida). Acarologia, 40, 237–264.
- Moraes, G.J. de, Denmark, H.A. & Guerrero, J.M. (1982) Phytoseiid mites of Colombia (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 8, 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958208683273
- Moraes, G.J. de, Alencar, J.A., Wenzel Neto, F. & Mergulhao, S.M.R. (1990) Explorations for natural enemies of the cassava green mite in Brazil. In: Howeler, R.H. (Ed.), Symposium of the International Society of Tropical Root Crops. International Society for Tropical Root Crops, Department of Agriculture, Bangkok, pp. 351–353.
- Moraes, G.J. de, McMurtry, J.A., Denmark, H.A. & Campos C.B. (2004) A revised catalog of the mite family Phytoseiidae. Zootaxa, 434 (1), 1–494. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.434.1.1
- Moraes, G.J. de, Zannou, I.D., Ueckermann, E.A., Oliveira, A.R., Yaninek, J.S. & Hanna, R. (2007) Phytoseiid mites of the tribes Afroseiulini, Kampimodromini and Phytoseiulini, and complementary notes on mites of the tribes Euseiini and Neoseiulini (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from sub-Saharan Africa. Zootaxa, 1628 (1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1628.1.1
- Moraes, G.J. de, Castilho, R.C., Flechtmann, C.H.W, Demite, P.R. & Halliday, B. (2025) Progress in understanding the world mesostigmatic mites, with emphasis on the family Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata). Acarologia, 65, 647–676. https://doi.org/10.24349/q3gy-1vyg
- Moraes, G.J. de, Alencar, J.A., Lima, J.L.S., Yaninek, J.S. & Delalibera Jr., I. (1993) Alternative plant habitats for common phytoseiid predators of the cassava green mite (Acari: Phytoseiidae, Tetranychidae) in northeast Brazil. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 17, 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00156945
- Moraes, V.S., Nunes, S.N., Demite, P.R. & Daud, R.D. (2022) Vegetation structure define mite assemblage on plants: a case study in Cerrado biome. Entomological Communications, 4 (ec04029), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.37486/2675-1305.ec04029
- Muma, M.H. (1955) Phytoseiidae (Acarina) associated with citrus in Florida. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 48, 262–272. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/48.4.262
- Muma, M.H. (1961) Subfamilies, genera, species of Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Bulletin of the Florida State Museum, 5, 267–302. https://doi.org/10.58782/flmnh.tqpo4380
- Muma, M.H. (1963) The genus Galendromus Muma, 1961 (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Florida Entomologist, 46, 15–41. https://doi.org/10.2307/3493355
- Muma, M.H. (1964) Annotated list and keys to Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata) associated with Florida citrus. University of Florida Agricultrual Experiment Station Bulletin, 685, 1–42.
- Muma, M.H. & Denmark, H.A. (1962) Intraspecific variation in Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Florida Entomologist, 45, 57–65. https://doi.org/10.2307/3492217
- Muma, M.H. & Denmark, H.A. (1969) The conspicua species-group of Typhlodromina Muma, 1961. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 62, 406–413. https://doi.org/10.1093/aesa/62.2.406
- Muma, M.H. & Denmark, H.A. (1970) Phytoseiidae of Florida. Arthropods of Florida and Neighboring Land areas. Vol. 6. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Division of Plant Industry, Gainesville, Florida,150 pp.
- Narayanan, E.S., Kaur, R.B. & Ghai, S. (1960) Importance of some taxonomic characters in the family Phytoseiidae Berl., 1916, (predatory mites) with new records and descriptions of species. Proceedings of the National Institute of Sciences of India, 26B, 384–394.
- Nuvoloni, F.M., Lofego, A.C., Rezende, J.M. & Feres, R.J.F. (2015a) Phytoseiidae mites associated with Hevea spp. from the Amazon region: a hidden diversity under the canopy of native trees. Systematics and Biodiversity, 13, 182–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/14772000.2014.985344
- Nuvoloni, F.M., Lofego, A.C., Castro, E.B. & Feres, R.J.F. (2015b) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) from rubber tree crops in the State of Bahia, Brazil, with description of two new species. Zootaxa, 3964 (2), 260–274. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3964.2.6
- Oliveira, D.C., Charanasri, V., Kongchuensin, M, Konvipasruang, P., Chandrapatya, A. & Moraes, G.J. de (2012) Phytoseiidae of Thailand (Acari: Mesostigmata), with a key for their identification. Zootaxa, 3453 (1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3453.1.1
- Onzo, A., Hanna, R., Zannou, I., Sabelis, M.W. & Yaninek, J.S. (2003a) Dynamics of refuge use: diurnal, vertical migration by predatory and herbivorous mites within cassava plants. Oikos, 101, 59–69. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.12572.x
- Onzo, A., Hanna, R. & Sabelis, M.W. (2003b) Interactions in an acarine predator guild: impact on Typhlodromalus aripo abundance and biological control of cassava green mite in Benin, West Africa. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 31, 225–241. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:APPA.0000010380.44408.05
- Rêgo, A.S., Maciel, A.G.S., Costa, E.C. & Silva, E.A. (2012) Comparative biology and growth rate of the mites Mononychellus tanajoa and Euseius ho (Acari) on cassava. Revista Colombiana de Entomología, 38, 243–246. https://doi.org/10.25100/socolen.v38i2.8999
- Reichert, M.B., Silva, G.L., Rocha, M.D.S., Johann, L. & Ferla, N.J. (2014) Mite fauna (Acari) in soybean agroecosystem in the northwestern region of Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 19, 123–136. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.19.2.2
- Rezende, J.M. & Lofego, A.C. (2011) Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata) on plants of the Central region of the Brasilian Cerrado. Acarologia, 51, 449–463. https://doi.org/10.1051/acarologia/20112027
- Rocha, M.D.S., Silva, G.L.D, Silva, J.O., Freitas, E.M. & Ferla, N.J. (2015) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in the northern coastal region of the Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. Neotropical Biodiversity, 1, 22–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/23766808.2015.1052230
- Rodrigues, J.K., Furtado, I.P. & Lofego, A.C. (2020) Mites (Arachnida: Acari) associated with plants of family Myrtaceae from the Caatinga Domain, Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 25, 942–956. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.25.5.14
- Rodrigues, J. K., Almeida-Neto, M., Demite, P.R., Silva, L.R.A., Araújo, I.F., Castro, E. B., Gondim Jr. M.G.C & Lofego, A.C. (2025) Mites on Caatinga remnants vegetation in Northeast Brazil, with description of a new species of Phytoseiidae (Acari: Mesostigmata). Systematic & Applied Acarology, 30, 243–266. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.30.2.5
- Rossetti, O.C., Araújo, F.G., Araújo W.S. & Daud, R.D. (2025a) Plant mites (Arachnida: Acariformes, Parasitiformes) in Caatinga remnants from Piauí State, Brazil. Papéis Avulsos de Zoologia, 65, e202565032. https://doi.org/10.11606/1807-0205/2025.65.032
- Rossetti, O.C., Barroso, G., Demite, P.R., Lima, E.L. & Daud, R.D. (2025b) Phytoseiidae mite (Parasitiformes: Phytoseiidae) assemblages from different Cerrado vegetation types. Acarologia, 65, 505–518. https://doi.org/10.24349/3rdh-xfoj
- Rowell, H.J., Chant, D.A. & Hansell, R.I.C. (1978) The determination of setal homologies, setal patterns on the dorsal shild in the family Phytoseiidae (Acarina: Mesostigmata). Canadian Entomologist, 110, 859–876. https://doi.org/10.4039/Ent110859-8
- Schmidt, R.A. (2014) Leaf structures affect predatory mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and biological control: a review. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 62, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-013-9730-6
- Schicha, E. & Corpuz-Raros, L.A. (1985) Contribution to the knowledge of the genus Paraphytoseius Swirski and Shechter (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). International Journal of Acarology, 11, 67–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647958508683398.
- Silva, J.M.C., Leal, I.R. & Tabarelli, M. (2018) Caatinga: the largest tropical dry forest region in South America. Springer, Cham, 503 pp.
- Silva, L.R.A., Gondim Jr., M.G.C. & Demite, P.R. (2023a) A new species of Galendromus Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from the Caatinga biome, Brazil. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 28, 258–268. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.28.2.9
- Silva, L.R.A., Gondim Jr., M.G.C. & Demite, P.R. (2024) A new species of Galendromimus Muma (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from the Caatinga biome, Brazil. Acarologia, 64, 32–39. https://doi.org/10.24349/cny5-hj6f
- Silva, E.A., Reis, P.R., Zacarias, M.S. & Marafeli, P.P. (2010) Fitoseídeos (Acari: Phytoseiidae) associados a cafezais, fragmentos florestais vizinhos. Ciência, Agrotecnologia, 34, 1146–1153. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542010000500010
- Silva, L.R.A., Silva, E.S., Marticorena, J.L. & Moraes, G.J. de (2021) A new species of Neoparaphytoseius (Acari: Mesostigmata: Phytoseiidae) from Brazil, with a review of the genus. Zootaxa, 4985 (2), 235–244. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4985.2.6
- Silva, J.M.C., Tabarelli, M., Fonseca, M.T. & Lins, L.V. (2003) Biodiversidade da Caatinga: Áreas, Ações Prioritárias Para a Conservação. Ministério do Meio Ambiente, Brasília, 382 pp.
- Silva, R.T.L., Berté, A.L.W., Bizarro, G.L., Schussler, M., Silva, D.E., Granich, J. & Ferla, N.J. (2023b) Mites associated with Vitis labrusca (Vitaceae) in southern Brazil: Population dynamics and ecology. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 28, 985–994. https://doi.org/10.11158/saa.28.6.1
- Sousa, J.M.D., Gondim Jr., M.G.C., Lofego, A.C. & Moraes, G.J. de (2015) Mites on Annonaceae species in northeast Brazil and in the state of Para. Acarologia, 55, 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1051/acarologia/20152147
- Souza, I.V., Oliveira, A.R. & Gondim Jr., M.G.C. (2010) A new species of the genus Typhlodromips De Leon (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from the state of Bahia, Brazil. International Journal of Acarology, 36, 49–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647950903508490
- Souza, I.V., Argolo, P.S., Gondim Jr., M.G.C., Moraes, G.J. de, Bittencourt, M.A.L & Oliveira, A.R. (2015) Phytoseiid mites from tropical fruit trees in Bahia State, Brazil (Acari, Phytoseiidae). ZooKeys, 533, 99–131. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.533.5981
- Swirski, E. & Shechter, R. (1961) Some phytoseiid mites (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) of Hong-Kong, with a description of a new genus, seven new species. Israel Journal of Agricultural Research, 11, 97–117.
- Tabarelli, M., Leal, I.R., Scarano, F.R. & Silva, J. (2018) Caatinga: legado, trajetória, desafios rumo à sustentabilidade. Ciência, Cultura, 70 (4), 25–29. https://doi.org/10.21800/2317-66602018000400009
- Teixeira, J.V., Ribeiro, R.N. & Daud, R.D. (2017) Mites on Curatella americana L. (Dilleniaceae) from Cerrado vegetation remnants in mining site vicinities. International Journal of Acarology, 43, 302–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2017.1284899
- Tixier, M-S., Kreiter, S., Barrau, J-N., Cheval, B. & Lecareux, C. (2005) Phytoseiid communities in southern France on vine cultivars and uncultivated surrounding areas. Acarologia, 46, 157–168.
- Toldi, M., Bizarro, G.L., Da-Costa, T., Silva V.L, Ferla, J.J., Johann, L., Freitas, E.M., Silva, G.L. & Ferla, N.J. (2021) Mite fauna associated com different environments in the Southern Pampa, Brasil. International Journal of Acarology, 47(5), 387–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/01647954.2021.1915378
- Trincado, R.D., Martin, J.P.I., Rosa, D.D.M., Lopes, P.C. & Moraes, G.J. de (2018) Phytoseiid mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae) from Chile, with descriptions of three new species and a redescription of Chileseius camposi. Zootaxa, 4482 (2), 322–340. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4482.2.5
- Van der Merwe, G.G. (1968) A taxonomic study of the family Phytoseiidae (Acari) in South Africa with contributions to the biology of two species. Department of Agricultural Technical Services, Entomology Memoirs, 18, 1–198.
- Vasconcelos, G.J.N. de, Silva, D.F., Barbosa, D.G.F., Gondim Jr., M.G.C. & Moraes, G.J. de (2006) Diversidade de fitoseídeos (Acari: Phytoseiidae) em fruteiras tropicais no Estado de Pernambuco, Brasil. Magistra, 18 (2), 90–101.
- Vasconcelos, G.J.N. de & Silva, N.D. (2015) Plant-inhabiting mites (Arachnida: Acari) in Amazonian agroecosystems In: Sant’Anna, B.S., Takeara, R. & Abegg, M.A. Amazonian Resources: microbiota, fauna, and flora. Nova Science, Hauppauge, pp. 99–113.
- Walter, D.E. & O’Dowd, D.J. (1992) Leaf morphology and predators: effect of leaf domatia on the abundance of predatory mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Environmental Entomology, 21, 478–484. https://doi.org/10.1093/ee/21.3.478
- Zacarias, M.S. & Moraes, G.J. de (2001) Phytoseiid mites (Acari) associated with rubber trees and other euphorbiaceous plants in southeastern Brazil. Neotropical Entomology, 30, 579–586. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-566X2001000400011
- Zundel, C., Hanna, R., Scheidegger, U. & Nagel, P. (2007) Living at the threshold: Where does the neotropical phytoseiid mite Typhlodromalus aripo survive the dry season? Experimental and Applied Acarology, 41, 11–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-007-9055-4