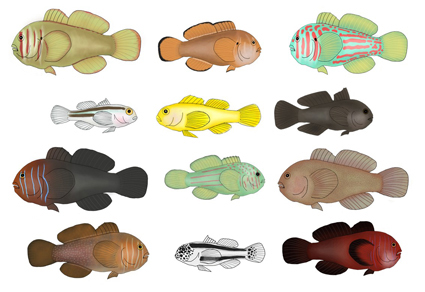
Abstract
Genus Gobiodon are obligate coral dwelling cryptic fishes. Gobiodon form a mutualistic relationship with host scleractinian corals, making them integral to coral reef ecosystem functioning. Despite this, they are often omitted from fish assemblage studies, biodiversity surveys and coral reef fish guides due to confusion on species identification. The guide aims to provide a comprehensive description of the main diagnostic features for the majority of Gobiodon species distributed throughout the Indo-Pacific region. Species of the genus can be observed occupying host corals of the genera Acropora, Stylophora, Hydnophora and Echinopora on coral reefs in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. Gobiodon species are known for their cryptic behaviours and are distinguishable using body colouration and colour markings. There are 31 described species, 26 of which have undisputed species status and sufficient data to include in this guide. We provide live colouration descriptions, known coral hosts, reef habitats and geographic ranges for each species. Recent developments in understanding the sociality and genetic relationships of this genus have also been incorporated. Useful field resources such as an identification key, occurrence table with accompanying map, and a colour plate of the encompassed species, have been included.
References
- Acero, A., Fricke, R., Larson, H.K. & Murdy, E. (2010) Gobiodon histrio: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2010, e.T154641A4595289.
- Akihito, S., Ikeda, Y. & Sugiyama, K. (2002) Gobiodei. In: Nakabo, T. (Ed.), Fishes of Japan with pictorial keys to the species. English edition. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, pp. 1139–1268.
- Allen, G.R. (2021) Gobiodon howsoni, a new species of coral reef fish (Gobiidae: Teleostei) from Rowley Shoals, Western Australia. Aqua, International Journal of Ichthyology, 27 (1), 11–20.
- Alleyne, H.G. & Macleay, W. (1877) The ichthyology of the Chevert expedition. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales, 1 (Pts. 3–4), 261–281 + 321–359, pls. 3–9 + 10–17. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.12420
- Avilés, L. & Harwood, G. (2012) A Quantitative Index of Sociality and Its Application to Group‐Living Spiders and Other Social Organisms. Edited by W. Koenig. Ethology, 118 (12), 1219–1229. https://doi.org/10.1111/eth.12028
- Bleeker, P. (1853) Nieuwe bijdrage tot de kennis der ichthijologische fauna van Ceram. Natuurkundig Tijdschrift voor Nederlandsch Indië. Available from: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=sourcedetails&id=431303 (accessed 21 September 2024)
- Bleeker, P. (1856) Bijdrage tot de kennis der ichthyologische fauna van het eiland Boeroe. Natuurkundig Tijdschrift Voor Nederlandsch Indië, 11 (2), 383–414.
- Bleeker, P. (1872–1973) Mémoire sur la faune ichthyologique de Chine. Nederlandsch Tijdschrift voor de Dierkunde, 4, 113–154.
- Bleeker, P. (1875) Gobioideorum species insulindicae novae. Archives néerlandaises des sciences exactes et naturelles, 10, 113–134.
- Brandl, S.J., Goatley, C.H.R., Bellwood, D.R. & Tornabene, L. (2018) The hidden half: ecology and evolution of cryptobenthic fishes on coral reefs. Biological Reviews, 93, 1846–1873. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12423
- Brook, G. (1891) Descriptions of new species of Madrepora in the collections of the British Museum. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 6, 8 (48), 458–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939109459223
- Brook, G. (1892) Preliminary descriptions of new species of Madrepora in the collections of the British Museum. Part II. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 6, 10 (60), 451–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939208677447
- Castelnau, F. comte de (1873) Contribution to the Ichthyology of Australia, Notes on Fishes from North Australia. Proceedings of the Zoological and Acclimatisation Society of Victoria, and report of the annual meeting of the society, II, 95–97.
- Castelnau, F. comte de (1873) Contribution to the ichthyology of Australia. No. I—The Melbourne Fish Market. Proceedings of the Zoological and Acclimatisation Society of Victoria, and report of the annual meeting of the society, 2, 37–158.
- Cuvier, G. & Valenciennes, A. (1837) Histoire naturelle des poissons. Tome douzième. Suite du livre quatorzième. Gobioïdes. Livre quinzième. Acanthoptérygiens à Pectorales Pédiculées, 1, 344–368.
- Dana, J.D. (1846–1849) Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838–1842. Vol. 7. Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 740 pp., 61 pls. [pp. 1–120 + 709–720 (1846), pp. 121–708 + 721–740 (1848), atlas pls. 1–61 (1849)]
- De Vis, C.W. (1884) Fishes from South Sea Islands. Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales, 3 (28–32).
- Dirnwöber, M. & Herler, J. (2007) Microhabitat specialisation and ecological consequences for coral gobies of the genus Gobiodon in the Gulf of Aqaba, northern Red Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 342 (July), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps342265
- Duchene, D., Klanten, S.O., Munday, P.L., Herler, J. & van Herwerden, L. (2013) Phylogenetic evidence for recent diversification of obligate coral-dwelling gobies compared with their host corals. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 69, 123–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2013.04.033
- Ehrenberg, C.G. (1834) Beiträge zur physiologischen Kenntniss der Corallenthiere im allgemeinen, und besonders des rothen Meeres, nebst einem Versuche zur physiologischen Systematik derselben. Abhandlungen der Königlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Berlin, 1, 225–380.
- Emery, A.R. & Winterbottom, R. (1986) Review of the gobioid fishes of the Chagos Archipelago, Central Indian Ocean. Royal Ontario Museum, Toronto, 82 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.52226
- Esper, E.J.C. (1797) Fortsetzungen der Pflanzenthiere in Abbildungennach der Natur mit Farben erleuchtet nebst Beschreibungen. Erster Theil. in der Raspischen Buchhandlung, Nürnberg, 230 pp., pls. XXXII–LXI. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.118730
- Esper, E.J.C. (1788–1830) Die Pflanzenthiere in Abbildungen nach der Natur mit Farben erleuchtet nebst Beschreibungen. 5 Vols. Raspischen Buchhandlung, Nuremberg. [text: 3 Vols., plates: 2 Vols.] Available from: https://digi.ub.uni-heidelberg.de/diglit/esper1791bd1 (accessed 28 October 2025) https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.118730
- Fischer von Waldheim, G. (1807) Museum Demidoff, ou, Catalogue systématique et raisonné des curiosités de la nature et de lart: données à l’Université Impériale de Moscou par son excellence Monsieur Paul de Demidoff. Tome III. Végétaux et Animaux. Imprimerie de Université Impériale de Moscou, Moscow, 300 pp., 6 pls. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.160942
- Fowler, H.W. (1944) Fishes obtained in the New Hebrides by Dr Edward L. Jackson. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia, 7, 1–408.
- Fricke, R., Eschmeyer, W.N. & Van der Laan, R. (Eds.), (2022) Eschmeyer’s Catalog of Fishes: Genera, Species, References. Available from: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/ (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Froehlich, C.Y.M., Klanten, O.S., Hing, M.L., Dowton, M. & Wong, M.Y.L. (2023) Delayed recovery and host specialization may spell disaster for coral‐fish mutualism. Ecology and Evolution, 13, e10209. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.10209
- Froehlich, C.Y.M., Heatwole, S.J., Selma Klanten, O., Hing, M.L., Hildebrandt, C.A., Smith, J.O. & Wong, M.Y.L. (2024) Multi‐level framework to assess social variation in response to ecological and social factors: modeled with coral gobies. Oikos, 2024 (10), e10669. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.10669
- Garman, S. (1903) Some Fishes from Australasia. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College, 39, 229–241.
- GBIF.Org (2024) Occurrence Download. The Global Biodiversity Information Facility. Available from: https://doi.org/10.15468/DL.PZJ6VD
- Gratzer, B., Millesi, E., Walzl, M. & Herler, J. (2015) Skin toxins in coral-associated Gobiodon species (Teleostei: Gobiidae) affect predator preference and prey survival. Marine Ecology, 36, 67–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/maec.12117
- Gray, J.E. (1840) Pocilloporidae. Synopsis of the Contents of the British Museum, 41, 54–84.
- Günther, A. (1861) Catalogue of the fishes in the British Museum. Catalogue of the acanthopterygian fishes in the collection of the British Museum. Gobiidae, Discoboli, Pediculati, Blenniidae, Labyrinthici, Mugilidae, Notacanthi. Department of Zoology, British Museum (Natural History), London, Preprint. Available from: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=sourcedetails&id=343236 (accessed 21 September 2024)
- Günther, A.C.L.G. (1861) Catalogue of the fishes in the British Museum. Department of Zoology, British Museum (Natural History), London. [unknown pagination] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.8809
- Harold, A.S., Winterbottom, R., Munday, P.L. & Chapman, R.W. (2008) Phylogenetic relationships of Indo-Pacific coral gobies of the genus Gobiodon (Teleostei: Gobiidae), based on morphological and molecular data. Bulletin of Marine Science, 82, 119–136.
- Harold, A.S. & Winterbottom, R. (1995) Gobiodon acicularis, a new species of gobioid fish (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from Belau, Micronesia. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 108 (4), 687–694.
- Harold, A.S. & Winterbottom, R. (1999) Gobiodon brochus: A New Species of Gobiid Fish (Teleostei: Gobioidei) from the Western South Pacific, with a Description of Its Unique Jaw Morphology. Copeia, 1999 (1), 49. https://doi.org/10.2307/1447384
- Herler, J., Bogorodsky, S.V. & Suzuki, T. (2013) Four new species of coral gobies (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Gobiodon), with comments on their relationships within the genus. Zootaxa, 3709 (4), 301–329. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3709.4.1
- Herler, J., Koblmüller, S. & Sturmbauer, C. (2009) Phylogenetic relationships of coral-associated gobies (Teleostei, Gobiidae) from the Red Sea based on mitochondrial DNA data. Marine Biology, 156 (4), 725–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-008-1124-7
- Herre, A.W.C.T. (1927) Gobies of the Philippines and the China Sea. Bureau of Science, Manila, Phillipine Islands, 23, 1–352.
- Hildebrandt, C.A., Froehlich, C.Y.M., Brodenicke, O.B., Klanten, O.S., Møller, P.R. & Wong, M.Y.L. (2024) Two new species of Gobiodon (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from the Indo-Pacific, with notes on South Pacific and Indian Ocean populations of Gobiodon spadix. Raffles Bulletin Of Zoology, 72, 488–510. https://doi.org/10.26107/RBZ-2024-0036
- Hing, M.L. (2019) The evolution of sociality in the genus Gobiodon and its maintenance under a changing climate. Doctor of Philosophy, University of Wollongong, Wollongong. [unknown pagination]
- Hing, M.L., Klanten, O.S., Wong, M.Y.L. & Dowton, M. (2019) Drivers of sociality in Gobiodon fishes: An assessment of phylogeny, ecology and life-history. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 137, 263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2019.05.020
- Hing, M.L., Selma Klanten, O., Dowton, M., Brown, K.R. & Wong, M.Y.L. (2018) Repeated cyclone events reveal potential causes of sociality in coral-dwelling Gobiodon fishes. PLoS ONE, 13 (9), e0202407. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202407
- Klunzinger, C.B. (1879) Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres. 2. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Erster Abschnitt: Die Madreporaceen und Oculinaceen. Gutmann, Berlin, 88 pp., 10 pls.
- Krøyer, H. (1845) Ichthyologiske Bidrag. Naturhistorisk Tidsskrift, Series II, 1, 213–282.
- Lamarck, J-B-P-A de M de (1816) Histoire naturelle des animaux sans vertèbres. Verdière, Paris, Vol. 2, 1–568.
- Larson, H. (2019a) Gobiodon ater. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T141483795A145090629.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019b) Gobiodon bilineatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T123434119A123494787.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019c) Gobiodon citrinus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019. Available from: https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/193106/2196006 (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019d) Gobiodon fuscoruber. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T141483816A147275210.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019e) Gobiodon irregularis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T123434776A123494797.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019f) Gobiodon okinawae. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T193112A2196805.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019g) Gobiodon prolixus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T193142A2200415.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019h) Gobiodon quinquestrigatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T193015A2184672.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019i) Gobiodon rivulatus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T193171A2204441.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2019j) Gobiodon winterbottomi. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 2019. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T141483916A148450941.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020a) Gobiodon acicularis: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T193147A2200875.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020b) Gobiodon aoyagii: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T141483785A145084911.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020c) Gobiodon axillaris. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T193222A2211025.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020d) Gobiodon brochus: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T193050A2188830.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020e) Gobiodon ceramensis: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T68330723A68333734.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020f) Gobiodon erythrospilus: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T68330883A68333739.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020g) Gobiodon fulvus: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T123434761A123494792.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020h) Gobiodon oculolineatus: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T68332134A68333754.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Larson, H. (2020i) Gobiodon reticulatus: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-2.RLTS.T46084436A46664619.en (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Masuda, H., Amaoka, K., Araga, C., Uyeno, T. & Yoshino, T. (1984) The fishes of the Japanese Archipelago. Tokai University Press, Tokyo, 437 pp.
- Milne Edwards, H. (1860) Histoire naturelle des coralliaires ou polypes proprement dits. Librairie Encyclopédique de Roret, Paris, 560 pp.
- Munday, P.L., Schubert, M., Baggio, J.A., Jones, G.P., Caley, M.J. & Grutter, A.S. (2003) Skin toxins and external parasitism of coral-dwelling gobies. Journal of Fish Biology, 62, 976–981. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8649.2003.00078.x
- Munday, P.L., Harold, A.S. & Winterbottom, R. (1999) Guide to coral-dwelling gobies, genus Gobiodon (Gobiidae) from Papua New Guinea and the Great Barrier Reef. Revue Francaise dAquariologie Herpetologie, 26 (1–2), 53–58.
- Munday, P.L., Jones, G.P. & Caley, M.J. (1997) Habitat specialisation and the distribution and abundance of coral-dwelling gobies. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 152, 227–239. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps152227
- Munday, P.L., Van Herwerden, L. & Dudgeon, C.L. (2004) Evidence for Sympatric Speciation by Host Shift in the Sea. Current Biology, 14 (16), 1498–1504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.029
- Munday, P.L. & Wilson, S.K. (1997) Comparative efficacy of clove oil and other chemicals in anaesthetization of Pomacentrus amboinensis, a coral reef fish. Journal of Fish Biology, 51 (5), 931–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1997.tb01532.x
- Nemenzo, F. (1959) Systematic studies on Philippine shallow water scleractinians: II. Suborder Faviida. Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines, 16, 73–135, pls. 1–24.
- Nemenzo, F. (1976) Some new Philippine scleractinian reef corals. Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines, 28, 229–276, pls. 1–10.
- Oken, L. (1815-1816) Lehrbuch der Naturgeschichte. Dritter Theil: Zoologie. Erste Abtheilung: Fleischlose Thiere. C.H. Reclam & A. Schmid, Leipzig/Jena, xxviii + 842 + xviii pp., 40 pls.
- Pereira, P.H.C. & Munday, P.L. (2016) Coral colony size and structure as determinants of habitat use and fitness of coral-dwelling fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 553 (July), 163–172. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps11745
- Playfair, R.L. & Günther, A. (1867) The fishes of Zanzibar, with a list of the fishes of the whole east coast of Africa. John Van Voorst, London, Preprint. Available from: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=sourcedetails&id=432362 (accessed 21 September 2024)
- Randall, J.E., Allen, G.R. & Steene, R.C. (1997) Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. Crawford House Press, Bathurst, New South Wales, 557 pp.
- Rüppell, E. & Vogel, F.C. (1838) Neue Wirbelthiere zu der Fauna von Abyssinien gehörig. S. Schmerber, Frankfurt am Main. [unknown pagination] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.53778
- Sato, M.C. & Motomura, H. (2024) Gobiodon spadix, a new coral goby (Teleostei: Gobiidae) from southern Japan. Ichthyology Research, 71, 422–431. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10228-024-00950-8
- Saville-Kent, W. (1893) The Great Barrier Reef of Australia; its products and potentialities. W.H. Allen, London, 387 pp., 48 pls., chromo pls. 1–16. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.58247
- Sawada, Y. & Arai, R. (1972) Gobiodon albofasciatus, a new coral goby from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Bulletin of the National Science Museum Tokyo, 15 (3), 415–420.
- Sawada, Y., Arai, R. & Abe, T. (1972) Gobiodon okinawae, a New Coral-Goby from the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Japanese Journal of Ichthyology, 19 (2), 57–62.
- Schweigger, A.F. (1820) Handbuch der Naturgeschichte der skelettlosen ungegliederten Thiere. Dykschen Buchhandlung, Leipzig, 776 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.59209
- Schiemer, L., Niedermüller, S. & Herler, J. (2009) The influence of colony size and coral health on the occupation of coral-associated gobies (Pisces: Gobiidae). Coral Reefs, 28 (1), 137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00338-008-0420-5
- Shibukawa, K., Suzuki, T. & Aizawa, M. (2013) Gobiodon aoyagii, a New Coral Goby (Actinopterygii, Gobiidae, Gobiinae) from the West Pacific, with Redescription of a Similarlycolored Congener Gobiodon erythrospilus Bleeker, 1875. Bulletin of the Museum of Natural Science, 39 (3), 143–165.
- Smith, J.L.B. (1959) Gobioid fishes of the families Gobiidae, Periophthalmidae, Trypauchenidae, Taenioididae and Kraemeriidae of the western Indian Ocean. Ichthyological Bulletin, Department of Ichthyology, Rhodes University, 13, 185–225, pls. 9–13.
- Studer, T. (1879) Zweite Abtheilung der Anthozoa Polyactinia, welche während der Reise A. M. S. Corvette Gazelle um die Erde gesammelt wurden. Monatsberichte der Königlich Preussischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin, 1878, 524–550, pls. 1–5.
- Suzuki, T., Yano, K. & Senou, H. (2012) Gobiodon winterbottomi, a New Goby (Actinopterygii: Perciformes: Gobiidae) from Iriomote-jima Island, the Ryukyu Islands, Japan. Bulletin of the Museum of Natural Science, Series A, (Supplementary 6), 59–65.
- Tornabene, L., Ahmadia, G.N., Berumen, M.L., Smith, D.J., Jompa, J. & Pezold, F. (2013) Evolution of microhabitat association and morphology in a diverse group of cryptobenthic coral reef fishes (Teleostei: Gobiidae: Eviota). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 66, 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2012.10.014
- Verrill, A.E. (1864) List of the polyps and corals sent by the Museum of Comparative Zoology to other institutions in exchange, with annotations. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, 1, 29–60. [in Chinese with English summary]
- Veron, J.E.N. (2000) Corals of the World. Vols. 1–3. Australian Institute of Marine Science and CRR, Queensland, xii + 463 pp., viii + 429 pp. & viii + 490 pp.
- Veron, J.E.N., Stafford-Smith, M.G., Turak, E. & DeVantier, L.M. (2024) Corals of the World. Version 0.01(Beta). Available from: http://coralsoftheworld.org/ (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Wallace, C.C. (1999) Staghorn corals of the world. A revision of the genus Acropora. CSIRO Publishing, Collingwood, 438 pp. https://doi.org/10.1071/9780643101388
- Weber, M. (1913) Die Fische der Siboga-Expedition. E. J. Brill, Leiden, xii + 710 pp., 12 pls.
- Winterbottom, R. & Harold, A.S. (2005) Gobiodon prolixus: A new species of gobiid fish (Teleostei: Perciformes: Gobiidae) from the Indo-west Pacific. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington, 118 (3), 582–589. https://doi.org/10.2988/0006-324X(2005)118[582:GPANSO]2.0.CO;2
- WoRMS Editorial Board (2024) World Register of Marine Species. Available from: https://www.marinespecies.org/imis.php?dasid=1447&doiid=170 (accessed 28 October 2025)
- Wu, H.-L. (1979) Description of two new species of Gobiodon Bleeker from China. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica. Available from: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=sourcedetails&id=427301 (accessed 21 September 2024)