Abstract
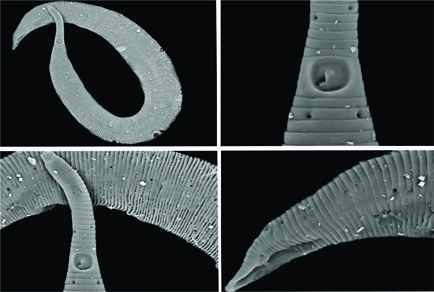
Three new species of the genus Rhynchonema Cobb, 1920 are described from sediment samples collected in the Potiguar Basin, Brazil. Rhynchonema brasiliensis sp. nov., is characterized by a circular amphideal fovea, located on an amphideal plate (wider cuticle annules which accommodate the entire fovea), short spicules, almost without curvature, gubernaculum with elongated dorsal apophysis and three precloacal supplements. Females are similar to males and have a vagina with visible sclerotization. Rhynchonema nordestinum sp. nov., has an oval amphideal fovea, robust and slightly curved spicules, and a gubernaculum with a dorsal apophysis. Rhynchonema parvum sp. nov., has a small and circular amphideal fovea, the smallest within the genus, thin and curved spicules, gubernaculum with a poorly developed dorsal apophysis. Rhynchonema species were separated into groups. These groupings were designated based on the morphological and morphometric characteristics considered most relevant for specific identification and they are presented as an illustrated key. The presence of an amphideal plate, the shape and size of the fovea, as well as the morphology of the males’ copulatory structures are examples of the characteristics used to establish groups of species. The diagnostic characteristics of all species were considered and used in the preparation of a comparative table.
References
- Abolafia, J. (2015) A low-cost technique to manufacture a container to process meiofauna for scanning electron microscopy. Microscopy Research and Technique, 78, 771–776. https://doi.org/10.1002/jemt.22538
- Allgén, C.A. (1940) Über einige neue freilebende Nematoden von der Nordwest- und Nordküste Norwegens. Folia Zoologica et Hydrobiologica, 10, 443–449.
- Aryuthaka, C. (1989) Two new species of the genus Rhynchonema (Nematoda, Xyalidae) from Amakusa, South Japan. Hydrobiologia, 171, 3–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005719
- Bezerra, T.N., Smol, N. & Vincx, M. (2014) Two new species of Rhynchonema Cobb, 1920 from a Brazilian sandy beach. Marine Biodiversity, 44, 343–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-014-0223-6
- Boucher, G. (1974) Six especes nouvelles du genre Rhynchonema (Rhynchonematinae - Nematoda). Cahiers de Biologie Marine, XV, 447–463.
- Chitwood, B.G. (1951) North American marine nematodes. Texas Journal of Science, 3, 627–672.
- Cobb, N.A. (1920) One hundred new nemas (type species of 100 new genera). Contribution to a Science of Nematology, IX, 217–343.
- Datta, T.K., De Jesús-Navarrete, A. & Mohapatra, A. (2015) Rhynchonema dighaensis sp. nov. (Monhysterida: Xyalidae): a marine nematode from the Indian coast with an illustrated guide and modified key for species of Rhynchonema Cobb, 1920. Zootaxa, 3905 (3), 365–380. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3905.3.3
- Decraemer, W. & Smol, N. (2006) Orders Chromadorida, Desmodorida and Desmoscolecida. In: Eyualem-Abebe, E.A., Traunspurger, W. & Andrássy, I. (Eds.), Freshwater Nematodes: Ecology and Taxonomy. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, pp. 497–573. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851990095.0497
- De Man, J.G. (1880) Die einheimischen, frei in der reinen Erde und im süßen Wasser lebenden Nematoden. Vorläufiger Bericht und deskriptiv-systematischer Teil. Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche Dierkundige Vereeniging, 5, 1–104.
- Fadeeva, N.P. & Karpova, A.A. (2024) New species of Metadesmolaimus, Rhynchonema and Gairleanema (Nematoda) from the sandy beaches of the Sea of Japan. Zootaxa, 5537 (1), 115–132. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5537.1.6
- Filipjev, I.N. (1929) Classification of free-living Nematoda and relations to parasitic forms. Journal of Parasitology Urbana, 15, 281–282.
- Fonseca, G. & Bezerra, T.N. (2014) Order Monhysterida. In: Shmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Ed.), Handbook of Zoology Gastrotricha, Cyclioneura and Gnathifera. Vol. 2. Nematoda. De Gruyter, Hamburg, pp. 435–465. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257.435
- Gagarin, V.G. (2020) New Genus and Two New Species of Free-Living Nematodes (Nematoda, Monhysterida) from Artificial Reservoirs in Vietnam. Inland Water Biology, 13 (1), 14–22. https://doi.org/10.1134/s1995082920010058
- Gerlach, S.A. (1953) Die Nematodenbesiedlung des Sandstrandes und des Küstengrundwassers an der italienischen Küste. I. Systematischer teil. Archivio Zoologico Italiano, 37, 517–640.
- Gourbault, N. (1982) Nématodes marins de Guadeloupe. I. Xyalidae nouveaux des genres Rhynchonema Cobb et Prorhynchonema nov. gen. Bulletin du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle Paris, 4, 75–87. https://doi.org/10.5962/p.286030
- Hodda, M. (2022) Phylum Nematoda: a classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa, 5114 (1), 1–289. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.1
- Hopper, B.E. (1961) Marine Nematodes from the coast line of Gulf of Mexico II. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 39, 359–365. https://doi.org/10.1139/z61-039
- Huang, H.L. & Liu, S.F. (2002) One new species of free-living marine nematodes from southeastern beach of Xiamen Island. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 21, 177–180.
- Inglis, W.G. (1983) An outline classification of the phylum Nematoda. Australian Journal of Zoology, 31, 243–255. https://doi.org/10.1071/ZO9830243
- Jiang, W. & Huang, Y. (2015) Paragnomoxyala gen. nov. (Xyalidae, Monhysterida, Nematoda) from the East China Sea. Zootaxa, 4039 (3), 467–474. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4039.3.6
- Knoppers, B., Ekau, W. & Figueiredo, A.G. (1999) A costa e a plataforma do leste e nordeste do Brasil e o transporte de materiais. Geo-Marine Letters, 19 (3), 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003670050106
- Leduc, D. (2015) One new genus and five new nematode species (Monhysterida, Xyalidae) from Tonga and Kermadec Trenches, Southwest Pacific. Zootaxa, 3964 (5), 501–525. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3964.5.1
- Leduc, D. (2023) New nematode species and genera (Nematoda: Chromadorea) from cold seeps on Hikurangi Margin, New Zealand. European Journal of Taxonomy, 856, 1–45. https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2023.856.2025
- Lorenzen, S. (1972) Die Nematodenfauna im Verklappungsgebiet für Industrieabwässer norwestlich von Helgoland I. Araeolaimida und Monhysterida. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 187, 223–248.
- Lorenzen, S. (1975) Rhynchonema–Arten (Nematodes, Monhysteridae) aus Südamerika und Europa. Mikrofauna Meeresboden, 55, 1–29.
- Lorenzen, S. (1977) Revision der Xyalidae (freilebende Nematoden) auf der Grundlage einer kritischen Analyse von 56 Arten aus Nord- und Ostsee. Veroff. Inst. Meeresforsch. Bremerh, 16, 197–261.
- Mota, J.T., Neres, P.F. & Esteves, A.M. (2025) Three new species of Rhynchonema (Monhysterida: Xyalidae) from the Brazilian continental shelf, Potiguar Basin. Zootaxa, 5604 (3), 285–308. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5604.3.4
- Murphy, D.G. (1964) Rhynchonema subsetosa, a new species of marine nematode, with a note on the genus Phylolaimus Murphy, 1963. Proceedings of Helminthological Society of Washington, 31, 26–28.
- Nemys, eds. (2025) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 17 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.14284/366
- Nicholas, W.L. & Stewart, A.C. (1995) New genera, species and new subfamily of Xyalidae (Nematoda: Monhysterida) from ocean beaches in Australia and Thailand. Transactions of the Royal Society of South Australia, 119, 47–66.
- Nicholas, W.L. & Trueman, J.W. (2002) The taxonomy of the family Xyalidae Chitwood, 1951 (Monhysterida: Nematoda): a cladistic analysis. Nematology, 4, 453–470. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854102760290446
- Somerfield, P.J., Warwick, R.M. & Moens, T. (2005) Meiofauna techniques. In: Eleftheriou, A. & McIntyre, A. (Eds.), Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos. 3rd Edition. Blackwell, Oxford, pp. 229–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/9780470995129.ch6
- Tauheed, U. & Ahmad, W. (2017) Three new species of the marine nematode genus Rhynchonema Cobb, 1920 (Nematoda: Monhysterida) from India. International Journal of Nematology, 27 (1–2), 7–21.
- Venekey, V., Gheller, P.F., Maria, T.F., Brustolin, M.C., Kandratavicius, N., Vieira, D.C., Brito, S., Souza, G.S. & Fonseca, G. (2014) The state of the art of Xyalidae (Nematoda, Monhysterida) with reference to the Brazilian records. Marine Biodiversity, 44, 367–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-014-0226-3
- Vitiello, P. (1967) Deux nouvelles spèces du genre Rhynchonema (Nematoda, Monhysteridae). Bulletin de la Societe Zoologique de France, 92, 113–121.
- Warwick, R.M., Platt, H.M. & Somerfield, P.J. (1998) Free-living Marine Nematodes Part III. Monhysterids. Synopses of the British fauna. New Series. Vol. 53. Field Studies Council, Shrewsbury, 296 pp.
- Yu, T. & Xu, K. (2015) Two new nematodes, Pseudelzalia longiseta gen. nov., sp. nov. and Paramonohystera sinica sp. nov. (Monhysterida: Xyalidae), from sediment in the East China Sea. Journal of Natural History, 49 (9–10), 509–526. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2014.953224