Abstract
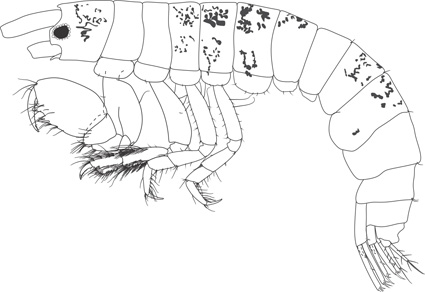
A wealth of shallow-water amphipod material was obtained during a 12-year survey (2012-2024) in the remote volcanic archipelago Trindade and Martin Vaz (TMV), located some 1200 km off the southeastern Brazilian coast. Three new species from Trindade Island in the genera Colomastix Grube, 1861 (Colomastigidae Chevreux, 1899), Pariphinotus Kunkel, 1910 (Phliantidae Stebbing, 1899) and Eusiroides Stebbing, 1888 (Pontogeneiidae Stebbing, 1906) were recently described, bringing the number of amphipod species from TMV to thirteen. Here we report on five new species from Trindade, three Aoridae Stebbing, 1899 (Bemlos myersi sp. nov., Globosolembos trindadensis sp. nov., Lembos quadrispinosus sp. nov.), and two Photidae Boeck, 1871 (Latigammaropsis oliveirai sp. nov., Latigammaropsis savioi sp. nov.).
References
- Afonso, O. (1976) Amphipoda des Açores cueillis par scaphandrier autonome (avec la description d’une nouvelle espèce). Publicaçioes do Instituto do Zoologia “Dr Augusto Nobre” Faculdade de Ciências do Porto, 130, 9–38.
- Alves, J., Nogueira, M.M., Neves, E.G. & Johnsson, R. (2023) A new genus of Aoridae and a new species of Bemlos Shoemaker, 1925 (Amphipoda: Senticaudata) from Northeastern Brazil. Marine Biodiversity, 53 (4), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-023-01357-w
- Ariyama, H. (2004) Two new species of the family Aoridae (Crustacea: Amphipoda) from the coasts of Wakayama and Osaka Prefectures, central Japan, with description of a new genus. Natural History Bulletin of Ibaraki University, 7, 1–16.
- Barnard, J.L. (1958) A remarkable new genus of corophiid amphipod from coastal marine bottoms of southern California. Bulletin of the Southern California Academy of Sciences, 57, 85–90, pls. 26–28.
- Barnard, K.H. (1916) Contributions to the Crustacean Fauna of South Africa n° 5. The Amphipoda. Annals of the South African Museum, 15 (3), 105–302.
- Boeck, A. (1861) Bemaerkninger angaaende de ved de norske Kyster forekommende Amphipoder. Forhandl. Skand. Naturf. Ott. Mode i Kjopenhavn, 8, 631–677.
- Boeck, A. (1871) Crustacea Amphipoda borealia et arctica. Forhandlinger i Videnskabs-Selskabet i Christiania, 1870, 81–280. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.2056
- Bynum, K.H. & Fox, R.S. (1977) New and noteworthy amphipod crustaceans from North Carolina, U.S.A. Chesapeake Science, 18, 1–33. https://doi.org/10.2307/1350362
- Bruzelius, R.M. (1859) Bidrag till Kännedomen om Skandinaviens Amphipoda Gammaridea. Kongliga Svenska Vetenskaps-Akademiens Handlingar, 3 (1), 1–104. [http://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/title/6480#page/7/mode/1up] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.28297
- Chevreux, E. (1901) Crustacés Amphipodes. Mission scientifique de M. Ch. Alluaud aux îles Séchelles (mars, avril, mai 1892). Mémoires de la Société entomologique de France, 14, 388–438.
- Grube, A.E. (1861) Ein Ausflug nach Triest und dem Quarnero. Beitrage zur Kenntniss der Thierwelt dieses Gebietes. Nicolaische verlagsbuchhandlung, Berlin, 175 pp., 5 pls. [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/6944841] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.7354
- Guedes–Silva, E., Souza–Filho, J.F. & Tavares, M. (2024) Three new species of Amphipoda (Crustacea: Peracarida) from the remote oceanic island of Trindade, off the coast of south-eastern Brazil. Journal of Natural History, 58 (45–48), 2075–2098. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2024.2410452
- Holmes, S.J. (1905) The Amphipoda of southern New England. Bulletin of the United States Bureau of Fisheries, 24, 457–529.
- Kunkel, B.W. (1910) The Amphipoda of Bermuda. Transactions of the Connecticut Academy of Arts and Sciences, 16, 1–116. [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/7321769]
- Latreille, P.A. (1816) Les Crustacés, les Arachnides, et les Insectes. In: Cuvier, G.L.C.F.D. (Ed.), Le Règne Animal, Distribué d’après son Organisation, pour Servrir de Base a l’Histoire Naturelle des Animaux et d’Introduction a l’Anatomie Comparée. Vol. 3. Deterville, Paris, pp. i–xxix+1–653. [dated 1817, published 2 December 1816 fide Roux, 1976]
- Lowry, J.K. & Myers, A.A. (2013) A Phylogeny and Classification of the Senticaudata subord. nov. (Crustacea: Amphipoda). Zootaxa, 3610 (1), 1–80. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3610.1.1
- Mateus, A. & Mateus, E.O. (1967) Amphipodes littoraux de Principe et de São Tomé. Annales de l’Institut Océanographique, 44, 173–198.
- Myers, A.A. (1985) Studies on the genus Lembos Bate. XI. Globosolembos sub-gen. nov. L. (G.) francanni Reid, L. (G.) indicus Ledoyer, L. (G.) ovatus sp. nov., L. (G.) tiafaui sp. nov., L. (G.) excavatus Myers. Bolletino del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Verona, 10, 341–367.
- Myers, A.A. (1988) A cladistic and biogeographic analysis of the Aorinae subfamily nov. Crustaceana, Supplement, 13, Studies on Amphipoda (Proceedings of the VIth International Colloquium on Amphipod Crustaceans, Ambleteuse, France, 28 June–3 July 1985), 167–192. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004629417_013
- Myers, A.A. (1995) The Amphipoda (Crustacea) of Madang Lagoon: Aoridae, Isaeidae, Ischyroceridae and Neomegamphopidae. Records of the Australian Museum, 1, 1–95. [http://www.australianmuseum.net.au/Uploads/Journals/17817/121_complete.pdf] https://doi.org/10.3853/j.0812-7387.22.1995.121
- Myers, A.A. (2009) Photidae. In: Lowry, J.K. & Myers, A.A. (Eds.), Benthic Amphipoda (Crustacea: Peracarida) of the Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Zootaxa, 2260 (1), 771–799. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2260.1.43
- Myers, A.A. (2014) Amphipoda (Crustacea) from the Chagos Archipelago. Zootaxa, 3754 (1), 1–31. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3754.1.1
- Nogueira, M.M., Alves, J., Neves, E. & Johnsson, R. (2021) The competition of native sponges and the sun coral Tubastraea spp. does not influence the morphological pattern of a new Photis (Photidae: Senticaudata). Journal of Natural History, 55 (33–34), 2065–2081. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2021.1973133
- Oliveira, L.P.H. (1955) Descrição e análise geométrica de Autonoe conicurvae, nova espécie de crustáceo (Amphipoda, Aoridae). Memórias do Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, 53 (2–3–4), 345–352. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02761955000200012
- Ruffo, S. (1969) Studi sui Crostacei anfipodi. 67. Terzo contributo alla conoscenza degli anfipodi del Mar Rosso. Memorie del Museo Civico di Storia Naturale, Verona, 17, 1–77. https://doi.org/10.1080/03749444.1982.10736661
- Schellenberg, A. (1925) Crustacea VIII: Amphipoda. L. Friedrichsen & Co, Hamburg, 93 pp., 27 figs. [pp. 111–204]
- Serejo, C.S. (1998) Gammaridean and caprellidean fauna (Crustacea) associated with the sponge Dysidea fragilis Johnston at Arraial do Cabo, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Bulletin of Marine Science, 63 (2), 363–385.
- Shoemaker, C.R. (1925) The Amphipoda collected by the United States Fisheries Steamer “Albatross” in 1911, chiefly in the Gulf of California. Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History, 52, 21–61.
- Shoemaker, C.R. (1942) Amphipod crustaceans collected on the Presidential Cruise of 1938. Smithsonian Miscellaneous Collections, 101 (11), 1–52, 17 figs.
- Souza–Filho, J.F. & Serejo, C.S. (2010) Two new species of the family Photidae (Amphipoda: Corophiidea: Photoidea) from Brazilian waters, with description of Rocasphotis gen. nov. Journal of Natural History, 44 (9–10), 559–577. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930903471118
- Souza–Filho, J.F. & Senna, A.R. (2012) First record of the genus Megamphopus Norman, 1869 (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Photidae) from Brazilian waters, with description of a new deep-sea species. Zoosystematics and Evolution, 88 (1), 71–77. https://doi.org/10.1002/zoos.201200008
- Spence Bate, C. & Westwood, J.O. (1861–1863) A History of the British Sessile-eyed Crustacea. Vol. 1. John Van Voorst, London, 507 pp. [https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/1936#/summary] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.9917
- Spence Bate, C.S. (1857) A synopsis of the British edriophthalmous Crustacea. Part I. Amphipoda. The Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 2, 19, 135–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222935708697715
- Stebbing, T.R.R. (1888) Report on the Amphipoda collected by H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–1876. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. Challenger during the years 1873–76, Zoology, 29 (Part 67), i–xxiv + 1–1737, pls. 1–212. http://19thcenturyscience.org/HMSC/HMSC-Reports/Zool-67/htm/doc.html
- Stebbing, T.R.R. (1899) Revision of Amphipoda (continued). Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 7, 4, 205–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939908678185
- Stephensen, K. (1948) Amphipods from Curaçao, Bonaire, Aruba and Margarita. Studies on the Fauna of Curaçao and Other Caribbean Islands, 3 (11), 1–20.
- Tavares, M. & Mendonça, J.B. (2022) Brachyuran crabs (Crustacea, Decapoda) from the remote oceanic Archipelago Trindade and Martin Vaz, South Atlantic Ocean. Zootaxa, 5146 (1), 1–129. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5146.1.1
- Valério-Berardo, M.T. & Flynn, M.N. (2002) Composition and seasonality of an Amphipod community associated to the algae Bryocladia trysigera. Brazilian Journal of Biology, 62 (4a). [published online] https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842002000400021
- Valério-Berardo, M.T. & Miyagi, V.K. (2000) Corophiidae (Crustacea, Amphipoda) da costa brasileira. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia, 17 (2), 481–504. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81752000000200019
- Watling, L. (1989) A classification of crustacean setae based on the homology concept. In: Felgenhauer, B.E., Watling, L. & Thistle, A.B. (Eds.), Functional Morphology of Feeding and Grooming in Crustacea. Vol. 6. CRC Press, London, pp. 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781003079354-2
- Wakabara, Y., Tararam, A.T., Valério-Berardo, M.T., Duleba, W. & Leite, F.P.P. (1991) Gammaridean and caprellidean fauna from Brazil. Hydrobiologia, 223, 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047629a
- Walker, A.O. (1898) Crustacea collected by W.A. Herdman, F.R.S., in Puget Sound, Pacific coast of North America, September 1897. Proceedings of the Liverpool Biological Society, 12, 268–287, 2 pls.