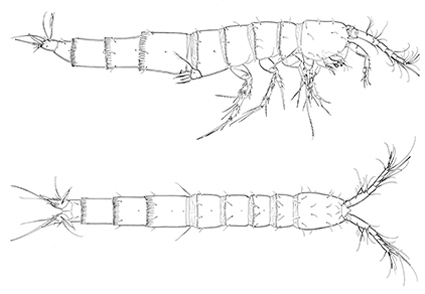
Abstract
A revision of the genus Arenopontia Kunz, 1937 (Harpacticoida, Arenopontiidae) is presented based on morphological examination of a wide range of material. The genus, as redefined herein, encompasses A. subterranea Kunz, 1937 (type species by monotypy), A. problematica Masry, 1970, A. nesaie Cottarelli, 1975 and A. riedli Lindgren, 1976, in addition to five new species from European waters: A. adriatica sp. nov., A. anatolica sp. nov., A. basibuyuki sp. nov., A. gunduzi sp. nov. and A. syltensis sp. nov. Arenopontia pontica Apostolov, 1969 is considered unidentifiable and confirmed as a species inquirenda. The widely accepted notion that A. subterranea represents a cosmopolitan species displaying high intraspecific variability is rejected. Previous illustrated records attributed to the type species are critically reassessed and indicate that future examination of additional material from sandy beaches in the Northern Hemisphere will lead to further splintering of “A. subterranea” into a complex of cryptic lineages. Arenopontia subterranea and A. syltensis sp. nov. occur sympatrically on the Isle of Sylt while extensive sampling in the Black Sea revealed a similar overlap in distribution between A. anatolica sp. nov. and A. basibuyuki sp. nov. This study provides yet another example of how rigorous morphology-based analysis of pseudocosmopolitan taxa allows resolution of previously unrecognized cryptic status into multiple named species without recourse to molecular sequence data. A key to the nine valid species of Arenopontia is presented and distribution data for each species are collated.
References
- Alper, A. (2009) Datça-Bozburun özel çevre koruma bölgesi (Muğla, Türkiye) sahillerinin kumiçi ve fital Harpacticoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) faunasının belirlenmesi. Determination of the interstitial and phytal Harpacticoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) fauna of the coast of Datça-Bozburun (Muğla, Turkey) specially protected area. PhD dissertation, University of Balıkesir, Balıkesir, 150 pp. [in Turkish with English summary]
- Alper, A., Karaytuğ, S. & Sak, S. (2010) Interstitial and phytal Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Copepoda) inhabiting the mediolittoral zone of the Datça-Bozburun peninsulas (Muğla, Turkey). SDU Journal of Science, 5 (1), 16–28.
- Alper, A., Sönmez, S., Sak, S. & Karaytuğ, S. (2015) Marine harpacticoid (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) fauna of the Dilek Peninsula (Aydın, Turkey). Turkish Journal of Zoology, 39, 580–586. https://doi.org/10.3906/zoo-1405-67
- Apostolov, A. (1969) Marine Harpacticoiden aus dem Küstensand von Bulgarien. Acta Musei macedonici Scientiarum naturalium, 11 (6), 111–130.
- Apostolov, A. (1970) Katalog der Harpacticoidenfauna Bulgariens. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 184, 412–427.
- Apostolov, A. (1971) Recherches sur la systématique et la distribution des Copépodes Harpacticoïdes de la côte bulgare. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 186, 337–347.
- Apostolov, A. (1973) Sur divers Harpacticoïdes (Copépodes) de la mer Noire. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 190, 88–110.
- Apostolov, A. (1982) Genres et sous-genres nouveaux de la famille Diosaccidae Sars et Cylindropsyllidae Sars, Lang. (Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Acta zoologica bulgarica, 19, 37–42.
- Apostolov, A. & Marinov, T.M. (1988) Copepoda Harpacticoida (morski kharpaktikoidi). [Copepoda, Harpacticoida (marine harpacticoids)]. Fauna Bolgarii [Fauna Bulgarica], 18, 1–384. [in Bulgarian].
- Arlt, G. (1983) Taxonomy and ecology of some harpacticoids (Crustacea, Copepoda) in the Baltic Sea and Kattegat. Zoologische Jahrbücher. Abteilung für Systematik, 110, 45–85.
- Bodin, Ph. (1968a) Copépodes Harpacticoïdes marins des substrats meubles des environs de la Rochelle. Note préliminaire. Recueil des Travaux de la Station Marine d’Endoume, 43 (59), 279–283.
- Bodin, Ph. (1968b) Copépodes Harpacticoïdes des étages bathyal et abyssal du golfe de Gascogne. Mémoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, Paris, nouvelle série, Series A, 55 (1), 1–107
- Bodin, Ph. (1979) Catalogue des nouveaux Copépodes Harpacticoïdes marins. (Nouvelle édition). Université de Bretagne Occidentale, Brest, 228 pp.
- Bodin, Ph. (1988) Results of ecological monitoring of three beaches polluted by the “Amoco Cadiz” oil spill: development of meiofauna from 1978 to 1984. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 42, 105–123. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps042105
- Bodiou, J.-Y. (1977) Harpacticoïdes (Crustacés, Copépodes) des îles Kerguelen. III. Description de deux formes nouvelles de la famille des Cylindropsyllidae. In: Le benthos du plateau continental des îles Kerguelen. CNFRA, 42, 277–286.
- Bodiou, J.-Y. & Colomines, J.-C. (1986) Harpacticoïdes (Copépodes) des Iles Crozet I. Description d’une espèce nouvelle du genre Arenopontia Kunz. Harpacticoids (Crustacea, Copepoda) from the Crozet Islands. Description of a new species of the genus Arenopontia Kunz. Vie et Milieu, 36, 55–64.
- Bonne, W. (2003) Benthische copepodengemeenschappen in relatie tot natuurlijke en anthropogene invloeden in the Noordzee. Sedimenten, zandontginning en de phytoplankton bloei. Benthic copepod communities in relation to natural and anthropogenic influences in the North Sea. Sediments, sand extraction and phytoplankton blooms. PhD dissertation, University of Gent, Belgium, 289 pp.
- Bruno, M.C., Cottarelli, V. & Berrera, R. (1998) Preliminary remarks on the cladistic systematics in some taxa of Leptopontiidae and Parastenocarididae (Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Bolletino. Museo Civico di Storia naturale di Verona, 2° Serie, 13, 69–79.
- Chappuis, P.-A. (1954a) IV. Copépodes psammiques des plages du Roussillon. In: P.-A. Chappuis & Cl. Delamare Deboutteville, avec la collaboration de J. Balazuc & S. Ruffo. Biospeologica LXXIV. Recherches sur les Crustacés souterrains (première série). Archives de Zoologie expérimentale et générale, 91, 35–50.
- Chappuis, P.-A. (1954b) Harpacticides psammiques récoltés par Cl. Delamare Deboutteville en Méditerranée. Vie et Milieu, 4, 254–276.
- Chappuis, P.-A. & Rouch, R. (1961) Harpacticides psammiques d’une plage près d’Accra (Ghana). Vie et Milieu, 11 (4), 605–614.
- Cottarelli, V. (1973) Paramesochridae (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) di acque interstiziali litorali Italiana. Rivista di Idrobiologia, 10 (1–2), 19–30.
- Cottarelli, V. (1975) Una nuova Arenopontia di acque interstiziali litorali della Sardegna (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Fragmenta entomologica, 11, 65–72.
- Cottarelli, V., Bruno, M.C. & Berera, R. (1998) Remarks on the genus Ichnusella (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida) and description of two new species from subterranean freshwater habitats in Latium and Sardinia, Italy. Vie et Milieu, 49, 129–143.
- Cottarelli, V., Bruno, M.C. & Venanzetti, F. (1994) Ricerche zoologiche della nave oceanografica “Minerva” (C.N.R.) sulle isole circumsarde. XVIII. First record in phreatic freshwater of harpacticoids belonging to the genus Arenopontia (Crustacea, Copepoda) and description of two new species. Annali del Museo civico di Storia naturale “Giacomo Doria”, 90, 471–485.
- Cottarelli, V. & Forniz, C. (1995) Ricerche zoologiche della nave oceanografica “Minerva” (C.N.R.) sulle isole circumsarde. XXIII. Meiopsyllus marinae: A new genus and a new species of Paramesochridae from the meiobenthos of Asinara and S. Pietro islands (Sardinia). Annali del Museo civico di Storia naturale “Giacomo Doria”, 90, 577–589.
- Cottarelli, V. & Venanzetti, F. (1989) Ricerche zoologiche della nave oceanografica «Minerva» (C.N.R.) sulle isole circumsarde. II. Cylindropsyllidae del meiobenthos di Montecristo e delle isole circumsarde (Crustacea, Copepoda, Harpacticoida). Annali del Museo civico di Storia naturale “Giacomo Doria”, 87, 183–235.
- Coull, B.C. (1971) Meiobenthic Harpacticoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) from the North Carolina continental shelf. Cahiers de Biologie marine, 12, 195–237. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.116176E2
- Coull, B.C. & Dudley, B.W. (1985) Dynamics of meiobenthic copepod populations: a long-term study (1973–1983). Marine Ecology Progress Series, 24, 219–229. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps024219
- Coull, B.C. & Herman, S.S. (1970) Zoogeography and parallel level-bottom communities of the meiobenthic Harpacticoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) of Bermuda. Oecologia, 5, 392–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00815503
- Darling, J.A. & Carlton, J.T. (2018) A framework for understanding marine cosmopolitanism in the Anthropocene. Frontiers in marine Science, 5, 293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00293
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1953a) La faune des eaux souterraines littorales des plages de Tunisie. Vie et Milieu, 4, 141–170.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1953b) Recherches sur l’écologie et la répartition du Mystacocaride Derocheilocaris remanei Delamare et Chappuis, en Méditerranée. Vie et Milieu, 4, 321–380.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1953c) La faune des eaux souterraines littorales en Algérie. Vie et Milieu, 4, 470–503.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1954) Premières recherches sur la faune souterraine littorale en Espagne. Publicaciones del Instituto de Biología Aplicada de Barcelona, 17, 119–129.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1955) Eaux souterraines littorales de la côte catalane française (Mise au point faunistique). Vie et Milieu, 5, 408–451.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1960a) Biologie des eaux souterraines littorales et continentales. Vie et Milieu, suppl. 9, 1–740.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl. (1960b) Arenopontia subterranea Kunz (Copepoda) présent à Madère. Vie et Milieu, 11 (2), 319.
- Delamare Deboutteville, Cl., Gerlach, S.A. & Siewing, R. (1955) Recherches sur la faune des eaux souterraines littorales du golfe de Gascogne. Littoral des Landes. In: Contribution à l’étude de la faune souterraine littorale. Vie et Milieu, 5 (3), 373–407.
- Galhano, M.H. (1970) Contribução para o conhecimento da fauna intersticial em Portugal. Publicações do Instituto de Zoologia “Dr. Augusto Nobre”, 110, 1–206.
- Gee, J.M. (1987) Impact of epibenthic predation on estuarine intertidal harpacticoid copepod populations. Marine Biology, 96, 497–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397967
- Giere, O. (1979) The impact of oil pollution on intertidal meiofauna. Field studies after the La Coruña-spill, May 1976. Cahiers de Biologie marine, 20, 231–251. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.EB86F35E
- Georgescu, A., Marcus, A. & Şerban, M. (1962) Les Harpacticoïdes de la R.P.R. Travaux du Muséum d’Histoire naturelle “Gr. Antipa”, 3, 75–92.
- Gerlach, S.A. (1977) Means of meiofauna dispersal. In: Sterrer, W. & Ax, P. (Eds.), The Meiofauna Species in Time and Space. Mikrofauna Meeresbodens, 61, 89–103.
- Goodman, K.S. (1980) The estimation of individual dry weight and standing crop of harpacticoid copepods. Hydrobiologia, 72, 253–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005629
- Griga, R.E. (1964) Copepoda donnykh biotsenozov Chernogo morya raiona evpatorii. Trudy Sevastopol’skoi biologicheskoi Stantsii, 15, 101–117. [in Russian]
- Harris, R.P. (1972) Horizontal and vertical distribution of the interstitial harpacticoid copepods of a sandy beach. Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 52, 375–387. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400018749
- Herman, R.L., Vanholsbeke, K. & Heip, C.H.R. (1986) Benthic studies of the Southern Bight of the North Sea. XI. The meiofauna in the Belgian coastal waters in the period 1980–1981. In: Heip, C.H.R. & Coomans, A. (Eds.), Ecology, Ecotoxicology and Systematics of marine Benthos. Laboratorium voor Morfologie en Systematiek der Dieren, Sektie Mariene Biologie Rijksuniversiteit Gent, Gent, pp. 39–54.
- Hockin, D.C. (1981) Maintenance of a diverse harpacticoid copepod community in microcosm culture. Marine Biology, 65, 209–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397087
- Hockin, D.C. (1982a) The spatial population structure of a harpacticoid copepod community in spring. Hydrobiologia, 96, 201–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010611
- Hockin, D.C. (1982b) The effect of sediment particle diameter upon the meiobenthic copepod community of an intertidal beach: a field and a laboratory experiment. Journal of animal Ecology, 51. 555–572. https://doi.org/10.2307/3984
- Hockin, D.C. (1982c) Further records of meiofauna predation and implications for the community stability. Crustaceana, 42, 106–108. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854082X00759
- Hockin, D.C. (1982d) The harpacticoid copepod fauna of the River Ythan and its estuary, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 62, 729–736. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400019883
- Hockin, D.C. (1983) The effects of organic enrichment upon a community of meiobenthic harpacticoid copepods. Marine environmental Research, 10, 45–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-1136(83)90016-8
- Hockin, D.C. & Ollason, J.C. (1981) The colonization of artificially isolated volumes of intertidal estuarine sand by harpacticoid copepods. Journal of experimental marine Biology and Ecology, 53, 9–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(81)90081-2
- Huys, R. (1992) The amphiatlantic distribution of Leptastacus macronyx (T. Scott, 1892) (Copepoda: Harpacticoida): a paradigm of taxonomic confusion; and a cladistic approach to the classification of the Leptastacidae Lang, 1948. Mededelingen van de Koninklijke Academie voor Wetenschappen, Letteren en Schone Kunsten van België, 4, 23–196.
- Huys, R. & Conroy-Dalton, S. (1996) A revision of Leptopontia T. Scott (Copepoda: Harpacticoida) with description of six new species. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 118, 197–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1996.tb01265.x
- Huys, R. & Conroy-Dalton, S. (2006) Revision of the genus Evansula T. Scott, 1906 (Copepoda, Harpacticoida, Cylindropsyllidae) with a description of three new species. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 147, 419–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2006.00227.x
- Huys, R. & De Smet, G. (1991) Meiobenthos van het Nederlands continentaal plat – Voorjaar 1991. Nederlands Instituut voor Oecologisch Onderzoek, Centrum voor Estuariene en Mariene Oecologie, Yerseke, 20 pp., tabs I–IX. [in Dutch]
- Huys, R., Gee, J.M., Moore, C.G. & Hamond, R. (1996) Marine and Brackish Water Harpacticoid Copepods. Part 1. In: Barnes, R.S.K. & Crothers, J.H. (Eds.), Synopses of the British Fauna. New Series. Vol. 51. Field Studies Council, Shrewsbury.i–viii + 352 pp.
- Huys, R., Herman, P.M.J., Heip, C.H.R. & Soetaert, K. (1992) The meiobenthos of the North Sea: density, biomass trends and distribution of copepod communities. ICES Journal of marine Science, 49, 23–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/49.1.23
- Huys, R. & Iliffe, T.M. (1998) Novocriniidae, a new family of harpacticoid copepods from anchihaline caves in Belize. Zoologica Scripta, 27, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1998.tb00425.x
- Joint, I.R., Gee, J.M. & Warwick, R.M. (1982) Determination of fine-scale vertical distribution of microbes and meiofauna in an intertidal sediment. Marine Biology, 72, 157–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396916
- Kunz, H. (1937) Zur Kenntnis der Harpacticoiden des Küstengrundwassers der Kieler Förde. (Studien an marinen Copepoden I.). Kieler Meeresforschungen, 2, 95–115.
- Kunz, H. (1975) Harpacticoiden (Crustacea, Copepoda) aus dem Küstengrundwasser der französischen Mittelmeerküste. Zoologica Scripta, 3, 257–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-6409.1974.tb00822.x
- Lampadariou, N., Tselepides, A. & Eleftheriou, A. (2005) Meiofauna in the Aegean Sea. In: Papathanassiou, E. & Zenetos, A. (Eds.), SoHelME, 2005. State of the Hellenic Marine Environment. Hellenic Centre for Marine Research Publishers, Anavissos, Attiki, pp. 220–225.
- Le Guellec, C. (1988) Colonisation d’un sable azoïque exogène par la méiofaune. Cahiers de Biologie marine, 29, 469–481. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.E6217CD6
- Lindgren, E.W. (1972) Systematics and ecology of North Carolina marine Sandy-beach Harpacticoida (Copepoda: Crustacea). PhD dissertation, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, 212 pp.
- Lindgren, E.W. (1976) Five species of Arenopontia (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) from a North Carolina beach, U.S.A. Crustaceana, 30, 229–240. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854076X00611
- McIntyre, A.D. (1977) Effects of pollution on inshore benthos. In: Coull, B.C. (Ed.), Ecology of Marine Benthos. Belle W. Baruch Library in Marine Science. No. 6. University of South Carolina Press, Columbia, pp. 301–318.
- McIntyre, A.D., Munro, A.L.S. & Steele, J.H. (1970) Energy flow in a sand ecosystem. In: Steele, J.H. (Ed.), Marine Food Chains. Proceedings International Symposium on Marine Food Chains. British Ecological Society, Aarhus, pp. 19–31.
- McIntyre, A.D. & Murison, D.J. (1973) The meiofauna of a flatfish nursery ground. Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 53, 93–118. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400056666
- McLachlan, A. & Furstenberg, J.P. (1977) Studies on the psammolittoral meiofauna of Algoa Bay. III. A quantitative analysis of the nematode and crustacean communities. Zoologica africana, 12, 61–71. https://doi.org/10.1080/00445096.1977.11447549
- Mantha, G., Moorthy, M.S.N., Altaff, K., Dahms, H.-U., Sivakumar, K. & Hwang, J.-S. (2012) Community structure of the Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Copepoda) on the coast of Chennai, India. Zoological Studies, 51, 463–475.
- Marinov, T.M. (1971) Kharpatikoidi ot b’lgarskoto kraibrezhnie na Cherno more [Harpacticoids of the Bulgarian Black Sea coast]. Izvestiya na Instituta Okeanografiya i Ribno Stopanstvo, Varna, 11, 43–87. [in Bulgarian with English and Russian summaries]
- Marinov, T. (1974) Quelques Harpacticides psammophiles inconnus pour le bassin de la mer Noire. Vie et Milieu, Series A, 23 (2), 309–326.
- Martínez Arbizu, P. & Moura, G. (1994) The phylogenetic position of the Cylindropsyllinae Sars (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) and the systematic status of the Leptopontiinae Lang. Zoologische Beiträge, Neue Folge, 35, 55–77.
- Masry, D. (1970) Ecological study of some sandy beaches along the Israeli Mediterranean coast, with a description of the interstitial harpacticoids (Crustacea, Copepoda). Cahiers de Biologie marine, 11, 229–258. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.4943D377
- Messana, G., Argano, R. & Baldari, F. (1978) Microcerberus (Crustacea Isopoda Microcerberidea) from the Indian Ocean (Pubblicazioni del Centro di Studio per la Faunistica ed Ecologia tropical del C.N.R.: CXXXIX). Monitore Zoologico Italiano Supplemento, 10, 69–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/03749444.1978.10736858
- Metin, O., Alper, A. & Sak, S. (2022) Interstitial harpacticoid (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) fauna inhabiting mediolittoral zone of the Gulf of Saros (Turkey). Saros Körfezi’nin (Türkiye) mediolitoral bölgesinde yaşayan kumiçi harpaktikoid (Copepoda, Harpacticoida) faunası. Balıkesir Üniversitesi Fen Bilimleri Enstitüsü. Dergisi [Journal of Balıkesir University, Institute of Science and Technology], 24, 779–790. https://doi.org/10.25092/baunfbed.1071262
- Michailova-Neikova, M. & Voinova-Stavreva, F. (1971) Prinos k’m izuchavane Harpacticoida (Crust., Copepoda) ot B’lgarskoto Chernomorsko kraibrezhie. Contribution to the study on Harpacticoida (Crust. Copepoda) of the Bulgarian Black Sea coast. Godishnik na Sofiìskiya Universitet, Biologiya [Annuaire de l’Université de Sofia, Biologie], 63 (1), 37–43.
- Mielke, W. (1975) Systematik der Copepoda eines Sandstrandes der Nordseeinsel Sylt. Mikrofauna des Meeresbodens, 52, 1–134.
- Mielke, W. (1976) Ökologie der Copepoda eines Sandstrandes der Nordseeinsel Sylt. Mikrofauna des Meeresbodens, 59, 1–86.
- Mielke, W. (1982) Interstitielle Fauna von Galapagos. XXIX. Darcythompsoniidae, Cylindropsyllidae (Harpacticoida). Mikrofauna des Meeresbodens, 87, 1–52.
- Mitwally, H.M. & Montagna, P.A. (2001) Egyptian interstitial Copepoda Harpacticoida with the description of two new species and one subspecies. Crustaceana, 74, 513–544. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854001300228825
- Moore, C.G. (1979) The zonation of psammolittoral harpacticoid copepods around the Isle of Man. Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 59, 711–724. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400045690
- Nagabhushanam, A.K. (1972) Studies on the marine intertidal ecology of the Orissa coast. Proceedings of the national Institute of Sciences of India, Biological Sciences, Series B, 38, 308–315.
- Nicholls, A.G. (1945) Marine Copepoda from Western Australia. IV.– Psammophilous harpacticoids. Journal of the Royal Society of Western Australia, 29, 17–24.
- Noodt, W. (1952) Marine Harpacticiden (Cop.) aus dem eulitoralen Sandstrand der Insel Sylt. Abhandlungen der mathematisch-naturwissenschaftlichen Klasse. Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur Mainz, 1952 (3), 105–142.
- Noodt, W. (1955a) Marmara denizi Harpacticoid’leri (Crust. Cop.). Marine Harpacticoiden (Crust. Cop.) aus dem Marmara Meer. Istanbul Üniversitesi Fen Fakültesi Mecmuası, Series B, 20, 49–94.
- Noodt, W. (1955b) Harpacticides (Crust. Cop.) psammiques de la côte sud-ouest de la France. Vie et Milieu, 6, 151–153.
- Noodt, W. (1955c) Harpacticiden (Crust. Cop.) aus dem Sandstrand der französischen Biscaya-Küste. Kieler Meeresforschungen, 11, 86–109.
- Noodt, W. (1956) Verzeichnis der im Eulitoral der schleswig-holsteinischen Küsten angetroffen Copepoda-Harpacticoidea. Schriften des naturwissenschaftlichen Vereins für Schleswig-Holstein, 28, 42–64.
- Noodt, W. (1957) Zur Ökologie der Harpacticoidea (Crust. Cop.) des Eulitorals der deutschen Meeresküste und der angrenzenden Brackgewässer. Zeitschrift für Morphologie und Ökologie der Tiere, 46, 149–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406967
- Noodt, W. (1962) Limnisch-subterrane Copepoden der Gattung Parastenocaris Kessler aus Mittelamerika. Beiträge zur Neotropischen Fauna, 2 (3), 223–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650526109380628
- Packmor, J. & George, K.H. (2018) Littoral Harpacticoida (Crustacea: Copepoda) of Madeira and Porto Santo (Portugal). Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 98, 171–182. [published online September 2016] https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315416001168
- Pennak, R.W. (1942) Harpacticoid copepods from some intertidal beaches near Woods Hole, Massachusetts. Transactions of the American microscopical Society, 61, 274–285. https://doi.org/10.2307/3222599
- Rao, G.C. (1967) On the life‑history of a new sand dwelling harpacticoid copepod. Crustaceana, 13, 129–136. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854067X00297
- Rao, G.C. (1968) On Psammothuria ganapatii n. gen. n. sp. an interstitial holothurian from the beach sands of Waltair coast and its autecology. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Series B, 67 (5), 201–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03053902
- Rao, G.C. (1970) The marine interstitial fauna inhabiting the beach sands of Orissa coast. Journal of the Zoological Society of India, 21, 89–104.
- Rao, G.C. (1975) The interstitial fauna in the intertidal sands of Andaman and Nicobar group of islands. Journal of the marine biological Association of India, 17, 116–128.
- Rao, G.C. (1980) On the zoogeography of the interstitial meiofauna of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Indian Ocean. Records of the Zoological Survey of India, 77, 153–178. https://doi.org/10.26515/rzsi/v77/i1-4/1979/161851
- Rao, G.C. (1987) Meiofauna of the Marine National Park, South Andaman. Journal of the Andaman scientific Association, 3, 88–97.
- Rao, G.C. (1989) Intertidal meiofauna. In: Jairajpuri, M.S. (Ed.), Fauna of Orissa. Part 2. State Fauna Series 1. Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta, pp. 1–77.
- Rao, G.C. (1991) Meiofauna. In: Jairajpuri, M.S. (Ed.), Fauna of Lakshadweep. State Fauna Series 2. Zoological Survey of India, Calcutta, pp. 41–135.
- Rao, G.C. & Ganapati, P.N. (1966) On a new species of Sphaerosyllis (Polychaeta) from the beach sands of Waltair coast. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Series B, 63 (6), 309–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03052366
- Rao, G.C. & Ganapati, P.N. (1968a) Some new interstitial gastrotrichs from the beach sands of Waltair coast. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Series B, 67 (2), 35–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03051683
- Rao, G.C. & Ganapati, P.N. (1968b) The interstitial fauna inhabiting the beach sands of Waltair coast. Proceedings of the National Institute of Sciences of India, Series B, 34 (2), 82–125.
- Rao, G.C. & Ganapati, P.N. (1969) On some interstitial copepods from the beach sands of Waltair coast. Proceedings of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Series B, 70, 262–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03052153
- Rao, G.C. & Misra, A. (1983) Meiofauna from Lakshadweep, Indian Ocean. Cahiers de Biologie marine, 24, 51–68. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.FAE78DC2
- Read, P.A., Anderson, K.J., Matthews, J.E., Watson, P.G., Halliday, M.C. & Shiells, G.M. (1983) Effects of pollution on the benthos of the Firth of Forth. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 14, 12–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(83)90088-7
- Renaud-Debyser, J. (1963a) Recherches écologiques sur la faune interstitielle des sables du Bassin d’Arcachon. Procès-verbaux de la Société Linnéenne de Bordeaux, 100, 75–82.
- Renaud-Debyser, J. (1963b) Recherches écologiques sur la faune interstitielle des sables. Bassin d’Arcachon – île de Bimini, Bahamas. Vie et Milieu, Supplement 15, 1–157.
- Renaud-Debyser, J. (1964) Note sur le faune interstitielle du Bassin d’Arcachon et description d’un Gastrotriche nouveau. Cahiers de Biologie marine, 5, 111–123. https://doi.org/10.21411/CBM.A.1DEC6636
- Renaud-Debyser, J. & Salvat, B. (1963) Éléments de prospérité des biotopes des sédiments meubles intertidaux et écologie de leurs populations en microfaune et macrofaune. Vie et Milieu, 14, 463–550.
- Rocha, C.E.F. da, Kihara, T.C., Sousa, R.M. Jr., Lotufo, G.R., Huys, R., Johnsson, R. & Björnberg, T.K.S. (2011) Copepoda. In: Amaral, A.C.Z. & Nallin, S.A.H. (Eds.), Biodiversidade e Ecossistemas bentônicos marinhos do Litoral Norte de São Paulo, Sudeste do Brasil. Marine benthic Biodiversity and Ecosystems from the northern coast of the State of São Paulo, southeastern Brazil. Instituto de Biologia. UNICAMP, Campinas, São Paulo, pp. 189–202.
- Rose, A. & Seifried, S. (2006) Small‑scale diversity of Harpacticoida (Crustacea, Copepoda) from an intertidal sandflat in the Jade Bay (German Bight, North Sea). Senckenbergiana maritima, 36, 109–122. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03043724
- Rouch, R. (1962) Harpacticoïdes (Crustacés Copépodes) d’Amérique du Sud. Biologie de l’Amérique Australe, 1, 237–280.
- Sak, S. (2004) Arenopontiidae (Copepoda: Harpacticoida) familyasının taksonomisi ve filogenisi. [Taxonomy and phylogeny of the family Arenopontiidae (Copepoda: Harpacticoida)]. PhD dissertation, University of Balıkesir, Türkiye, 312 pp.
- Sak, S., Huys, R. & Karaytuğ, S. (2008) Disentangling the subgeneric division of Arenopontia Kunz, 1937: resurrection of Psammoleptastacus Pennak, 1942, re-examination of Neoleptastacus spinicaudatus Nicholls, 1945, and proposal of two new genera and a new generic classification (Copepoda, Harpacticoida, Arenopontiidae). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 152, 409–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00373.x
- Samargiu, M. (2010) Interstitial harpacticoids from the shallow waters of the Romanian Black Sea coast. Rapports et Procès-verbaux des Réunions de la Commission internationale de la Mer Méditerranée, 39, 655.
- Schriever, G. (1984) The history of the copepod investigations at the Zoologisches Institut und Museum der Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel. In: Vervoort, W. & Vaupel Klein, J.C. von (Eds.), Studies on Copepoda II. Proceedings of the First International Conference on Copepoda, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–28 August 1981. Crustaceana, Supplement 7, pp. 371–376. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004629363_040
- Scott, T. (1892) Additions to the fauna of the Firth of Forth. Part IV. Report of the Fishery Board for Scotland, 10 (3), 244–272, pls. VII–XIII.
- Scott, T. (1902) Notes on gatherings of Crustacea collected by the Fishery Steamer “Garland” and the steam trawlers “Star of Peace” and “Star of Hope”, of Aberdeen, during the year 1901. Report of the Fishery Board for Scotland, 20 (3), 447–485, pls. XXII–XXV.
- Scott, T. (1906) A catalogue of the land, fresh-water and marine Crustacea found in the basin of the River Forth and its estuary. Proceedings of the Royal physical Society of Edinburgh, 16, 97–386, pl. VI. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.53706
- Segelken-Voigt, A., Gerdes, K., Wehrmann, A., Martínez Arbizu, P. & Glatzel, T. (2018) Light or tide? Effects on the emergence and recolonization of harpacticoid copepods from sand flats of the Wadden Sea (southern North Sea). Journal of experimental marine Biology and Ecology, 502, 52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2017.08.008
- Şerban, M. (1959) Les Copépodes de la mer Noire. Note préliminaire sur les Harpacticides de la côte Roumaine. Lucrǎrile sesiunii sţiinţifice (15–17 Sept. 1956) a Staţiunii zoologice marine “Prof. Ioan Borcea”, Agigea, Vol. Festival 1956, 259–302.
- Sevastou, K. (2005) On the ecology of meiofauna of the sandy shores of Crete: distribution patterns of meiobenthic copepods over space and time. PhD dissertation, University of Crete, Heraklion, Crete, 233 pp. [in Greek with English summary]
- Sevastou, K., Lampadariou, N. & Eleftheriou, A. (2011) Meiobenthic diversity in space and time: The case of harpacticoid copepods in two Mediterranean microtidal sandy beaches. Journal of Sea Research, 66, 205–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2011.06.004
- Sewell, R.B.S. (1940) Copepoda Harpacticoida. Scientific Reports of the John Murray Expedition, 7, 1l7–382.
- Smol, N. (1986) Rol van het meiozoobenthos in de Oosterschelde. Eindrapport BALANS 1986-14. Delta Instituut voor Hydrobiologisch Onderzoek, Yerseke, 148 pp., pls. 1–3. [in Dutch]
- Smol, N., Huys, R. & Vincx, M. (1989) Studie van het meiobenthos van een dumpingsgebied van titaandioxide-afval in de Nederlands kustwateren, periode 1986–1987. Rijksuniversiteit Gent, Laboratorium voor Morfologie en Systematiek der Dieren, Sectie Mariene Biologie, Gent, 64 pp., 32 tabs., 38 figs. [in Dutch]
- Sugumaran, J. & Padmasai, R. (2019) Meiofaunal diversity and density of Manamelkudi—an intertidal sandy beach of Palk Bay, India. Research Journal of Life Sciences, Bioinformatics, pharmaceutical and chemical Sciences, 5 (2), 31–46.
- Van Damme, D. & Heip, C. (1976) Het meiobenthos in de zuidelijke Noordzee. In: Nihoul, J.C.J. & De Coninck, L.A.P. (Eds.), Projekt Zee Eindverslag: 7. Inventaris van de Fauna en Flora, 1976, pp. 1–113. [in Dutch]
- Vijaya Bhanu, C.H., Srinivasa Rao, M., Annapurna, C., Satyanarayana, A., Ambedkar, A. & Chandra Rao, K. (2017) Checklist of harpacticoid copepods (Class: Crustacea) from Nizampatnam Bay, Bay of Bengal. Golden Research Thoughts, 6, 8.
- Vorobjeva, L.V. (1984) Raspredeleniya kopepod garpaktitsid v peschanykh plyazhakh Odesskogo poberezh’ya. The distribution of Copepoda (Harpacticoida) in sand of the north-west coast of the Black Sea. Biologiya Morya, Vladivostok, 1984 (3), 45–49. [in Russian with English summary, translation in Soviet Journal of marine Biology, 10 (3), 155–158 (as: Distribution of copepods (Harpacticoida) on the sandy beaches of the Odessan coast)]
- Wells, J.B.J. (1961) Interstitial copepods from the Isles of Scilly. Crustaceana, 2, 262–274. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854061X00392
- Wells, J.B.J. (1963) Copepoda from the littoral region of the estuary of the River Exe (Devon, England). Crustaceana, 5, 10–26. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854063X00020
- Wells, J.B.J. (1967) The littoral Copepoda (Crustacea) of Inhaca Island, Mozambique. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 67 (7), 189–358. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0080456800024017
- Wells, J.B.J. (1970) The marine flora and fauna of the Isles of Scilly. Crustacea: Copepoda: Harpacticoida. Journal of natural History, 4, 255–268. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222937000770251
- Wells, J.B.J. (1986a) Biogeography of benthic harpacticoid copepods of the marine littoral and continental shelf. In: Schriever, G., Schminke, H.K. & Shih, C.-T. (Eds.), Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Copepoda, Ottawa, Canada, 13–17 August, 1984. Syllogeus, No. 58. National Museums of Canada, National Museum of Natural Sciences, Ottawa, pp. 126–135.
- Wells, J.B.J. (1986b) Copepoda: Marine-interstitial Harpacticoida. In: Botosaneanu, L. (Ed.), Stygofauna Mundi, a faunistic, distributional, and ecological synthesis of the world fauna inhabiting subterranean waters (including the marine interstitial). E.J. Brill/Dr. W. Backhuys, Leiden, pp. 356–381.
- Wells, J.B.J. (2007) An annotated checklist and keys to the species of Copepoda Harpacticoida (Crustacea). Zootaxa, 1568 (1), 1–872. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1568.1.1
- Wells, J.B.J. & Clark, M.E. (1965) The interstitial Crustacea of two beaches in Portugal. Revista de biologia, Lisboa, 5, 87–108.
- Willems, K.A. (1981) Boreopontia heipi n. g., n. sp., an interstitial harpacticoid (Copepoda) from the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Biologisch Jaarboek Dodonaea, 49, 200–209.
- Willems, K.A., Vincx, M., Claeys, D., Vanosmael, C. & Heip, C. (1982) Meiobenthos of a sublittoral sandbank in the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Journal of the marine biological Association of the United Kingdom, 62, 535–548. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400019731
- Willems, W.R., Curini-Galletti, M., Ferrero, T.J., Fontaneto, D., Heiner, I., Huys, R., Ivanenko, V.N., Kristensen, R.M., Kånneby, V, MacNaughton, M.O., Martínez Arbizu, P., Todaro, M.A., Sterrer, W. & Jondelius, U. (2009) Meiofauna of the Koster-area, results from a workshop at the Sven Lovén Centre for Marine Sciences (Tjärnö, Sweden). Meiofauna marina, 17, 1–34.