Abstract
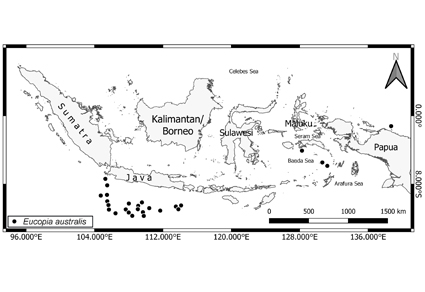
The zoogeographic distribution of lophogastrid species (Crustacea: Peracarida: Lophogastrida) occurring in the Indonesian waters is presented. For each species, data on general distribution, bathymetric ranges, habitat and localities reported on published data are provided. A total of 20 lophogastrid species belonging to three families and seven genera occur in Indonesian waters (about 38% of all known lophogastrids species worldwide), a number greater than other areas of Southeast Asia. Also, based on current information, the number of species or species richness is greater than other regions, such as Madagascar, North Pacific off Japan, Mediterranean, Canary Island, northern mid-Atlantic ridge, Iberian Peninsula, Mexico, and Angola Basin (SE Atlantic). Most of the Indonesian species are distributed worldwide, but one species, Lophogaster inermis appears to be endemic to Indonesia. Previous listings of Paralophogaster intermedius occurring in Southeast Asian waters is not verified in any collections, and has therefore been removed from our updated list.
References
- Aladin, N., Plotnikov, I., Bolshov, A. & Pichugin, A. (2006) Biodiversity of the Caspian Sea. In: Caspian Sea Biodiversity Project under umbrella of Caspian Sea Environment Program. Available from: https://www.zin.ru/projects/caspdiv/biodiversity_report.html (accessed 30 November 2022)
- Bamber, R.N. & Clark, P.F. (2004) A new species of Lophogaster (Crustacea, Mysidacea, Lophogastrida) from the equatorial eastern Atlantic. Zoosystema, 26 (3), 419–423.
- Banner, A.H. (1954) Some ‘schizopod’ crustaceans from the deeper water off California. Allan Hancock foundation Publications of the University of Southern California. Occasional Paper, 13, 1–48.
- Birstein, J.A. & Tchindonova, J.G. (1958) Glubocovodniie mysidii severo zapadnoi ciasti Tihogo Okeana (The deep sea mysids of the northwest Pacific Ocean). Trudy Instituta Okeanologii (Transactions of the Institute of Oceanology), 27, 258–355.
- Birstein, J.A. & Tchindonova, J.G. (1962) Mysidacea collected by the Soviet Antarctic Expedition on the M/V “Ob”. Rezul’taty biologicheskikh issledovanii Sovetskoi antarkticheskoi ekspeditsii, 1955–1958 (Biological reports of the Soviet Antarctic Expedition, 1955–1958), 1, 58–68.
- Boas, J.E.V. (1883) Studien über die Verwandtschaftsbeziehungen der Malakostraken. Morphologisches Jahrbuch, 8 (4), 485–579.
- Brusca, R.C. & Brusca, G.J. (2003) Invertebrates. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts, xix + 936 pp.
- Băcescu, M. (1981) Résultats de les campagnes Musorstom I - Philippines (18–28 mars 1976), Crustacea Mysidacea. Collection Mémoires ORSTOM, 91, 261–276.
- Băcescu, M. (1985) Crustacés Mysidacés [MUSORSTOM II].—In: Résultats des Campagnes MUSORSTOM II.—Mémoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, Series A, Zoologie, 133, 355–366.
- Băcescu, M. (1991) Crustacea Mysidacea: Récoltes faites au cours des campagnes Musorstom 3 et Corindon 2 aux Philippines et en Indonésie. In: Crosnier, A. (Ed.), Résultats des Campagnes Musorstom. Vol. 9. Mémoires Muséum national d’histoire naturelle, Série A, 152, pp. 79–100.
- Calman, W.T. (1904) On the classification of Malacostraca. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, Series 7, 13, 144–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930408562451
- Casanova, J.-P. (1993) Crustacea Mysidacea: Les Mysidacés Lophogastrida et Mysida (Petalophthalmidae) de la région néocalédonienne. In: Crosnier, A. (Ed.), Résultats des Campagnes MUSORSTOM, 10. Memoires du Muséum national d’Histoire naturelle, 156, pp. 33–53.
- Casanova, J.-P. (1996) Crustacea Mysidacea: Les Lophogastridés d’indonésie, de Nouvelle- Calédonie et des îles Wallis et Futuna. In: Crosnier, A. (ed.), Resultats des Campagnes Musorstom. Vol. 15. Mémoires du Muséum national d´Histoire naturelle, 168, 125–146.
- Casanova, J.-P. (1997) Les mysidacés Lophogastrida (Crustacea) du canal de Mozambique (côte de Madagascar). Zoosystema, 19 (1), 91‒109.
- Coifmann, I. (1937) I misidacei del Mar Rosso. Studio del materiale raccolte dal Prof. L. Sanzo durante la campagne idrografica della R. Nave Ammiraglio Magnaghi (1923-1924). Memoirs Regio Comitato Talassografico Italiano, 233, 1–52, 25 pls.
- Dana, J.D. (1852) United States Exploring Expedition, during the years 1838, 1839, 1840, 1841, 1842. Under the command of Charles Wilkes, U.S.N. XIII. Crustacea. Part I. Printed by C. Sherman, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, VIII + 685 pp.
- Dohrn, A. (1870) Untersuchungen über Bau und Entwicklung der Arthropoden. 10. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Malacostraken und ihrer Larven. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie, 20, 607–626, taf. XXX–XXXII.
- Fage, L. (1939) A propos d’un mysidacé bathypélagique peu connu: Chalaraspis alata G. O Sars (Willemoes-Suhm in lit). Archives de Zoologie expérimentale et Générale (Notes et revue), 80, 68–76.
- Fage, L. (1940) Diagnoses préliminaires de quelques espèces nouvelles du genre Lophogaster (Crust. Mysidacés). Bulletin du Muséum, 2, XII (6), 323–328.
- Fage, L. (1941) Mysidacea Lophogastrida I. The Carlsberg Foundation’s oceanographical expedition round the world 1928–30 and previous “Dana”-expeditions. Copenhagen and London, C.A. Reitzels Forlag and Oxford University Press. Dana Reports, 19, 1–52.
- Fage, L. (1942) Mysidacea Lophogastrida. II. The Carlsberg Foundation’s oceanographical expedition round the world 1928–1930 and previous “Dana” expeditions under the leadership of Prof. Johannes Schmidt. Dana Report, 23, 1–67.
- Faxon, W. (1893) Reports on the dredging operations off the west coast off Central America to the Galápagos, to the west coast of Mexico, and the Gulf of California; in charge of Alexander Agassiz, carried on by the U.S. Fish Commission Steamer “Albatross” during 1891. VI. Preliminary descriptions of new species of Crustacea. Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology, 24, 149–220.
- Faxon, W. (1895) Reports on an exploration off the west coasts of Mexico, Central and South America, and off the Galápagos Islands in charge of Alexander Agassiz, by the U.S. Fish Commission Steamer “Albatross”, during 1891, Lieut.-Commander Z.L. Tanner, U.S.N., Commanding. XV The Stalk-eyed Crustacea. Memoirs of the Museum of Comparative Zoology Harvard, 18, 1–292.
- Fukuoka, K. (2009) Deep-sea mysidaceans (Crustacea: Lophogastrida and Mysida) from the Northwestern North Pacific off Japan, with descriptions of six new species. In: Fujita, T. (Ed.), Deep-sea Fauna and Pollutants off Pacific Coast of Northern Japan. National Museum of Nature and Science Monographs, No. 39, pp. 405–446.
- Fukuoka, K. & Murano, M. (2002) Mysidacea (Crustacea) from the south-eastern Andaman Sea with descriptions of six new species. Phuket Marine Biological Center Special Publication, 23 (1), 53–108.
- Hansen, H.J. (1905) Preliminary report on the Schizopoda collected by H.S.H. Prince Albert of Monaco during the cruise of the Prince-Alicce in the year 1904. Bulletin du Musée Océnographique de Monaco, 30, 1–32.
- Hansen, H.J. (1910) The Schizopoda of the Siboga Expedition1899–1900. Siboga Expeditie, 37, 1–120. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.10421
- Hansen, H.J. (1912) Reports on the scientific results of the expedition to the eastern tropical Pacific by the U. S. Fish Commission Steamer Albatross: The Schizopoda. Memoirs of the Museum of Comparative Anatomy at Harvard College, 35, 175–296.
- Hendrickx, M.E. (2019) Species of Gnathophausiidae (Crustacea, Lophogastrida) collected off the west coast of Baja California, Mexico, during the TALUD cruises. Zootaxa, 4609 (3), 449–468. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4609.3.3
- Hernández-Payán, J.C. & Hendrickx, M.E. (2020) Revaluación de la fauna de Lophogastrida y Mysida (Crustacea: Peracarida) del Pacífico mexicano (Revaluation of the fauna of Lophogastrida and Mysida (Crustacea: Peracarida) of the Mexican Pacific). Geomare Zoologica, 2 (3), 49‒59.
- Illig, G. (1906) Ein Weiterer Bericht üeber die Schizopoden der Deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition 1898–1899. Supplement 1. 2. Gnathophausien. Zoologischer Anzeiger, 30, 227–322.
- Illig, G. (1930) Die Schizopoden der Deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der Deutschen Tiefsee Expedition “Valdivia”, 22 (6), 397–625.
- Mauchline, J. (1980) Part one. The biology of mysids. In: Blaxter, J.H.S., Russell, F.S. & Yonge, M. (Eds.), The Biology of Mysids and Euphausiids. Advance in Marine Biology Vol. 18. Academic Press, London, pp. 1–369.
- Mees, J. & Meland, K. (Eds.) (2023) World List of Lophogastrida, Stygiomysida and Mysida. Available from https://www.marinespecies.org/mysidacea (accessed 10 February 2023)
- Meland, K. & Aas, P.Ø. (2013) A taxonomical review of the Gnathophausia (Crustacea, Lophogastrida), with new records from the northern mid-Atlantic ridge. Zootaxa, 3664 (2), 199‒225. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3664.2.5
- Meland, K. & Willassen, E. (2007). The disunity of “Mysidacea” (Crustacea). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 44 (3), 1083–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2007.02.009
- Müller, H.-G. (1993) World Catalogue and Bibliography of the Recent Mysidacea. Laboratory for Tropical Ecosystems Research and Information Service, Vetzlar, 491 pp.
- Nouvel, H. (1942) Sur al systématique des espèces du genre Eucopia Dana 1852 (Crust. Mysidacea). Bulletin de l´Institut Océanographique, 818, 1–9.
- Nouvel, H., Casanova, J.-P. & Lagardère, J.-P. (1999) Ordre des Mysidacés (Mysidacea Boas, 1883). Mémoires de l’ Institut Océanographique, Monaco, 19, 39–86.
- Petryashov, V.V. (1992) Notes on mysid systematics (Crustacea, Mysidacea) of Arctic and the north-western Pacific. Zoologichesky Zhurnal, 71 (10), 47–58.
- Petryashov, V.V. (2015) Taxonomy of Family Gnathophausiidae (Crustacea: Lophogastrida). Russian Journal of Marine Biology, 41 (4), 238–243. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074015040112
- Price, W.W. & Heard, R.W. (2009) Mysida (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. In: Felder, D.L. & Camp, D.K. (Eds.), Gulf of Mexico—origins, waters, and biota. Biodiversity 1. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas, pp. 929–938.
- Price, W.W., Heard, R.W., Aas, P.Ø. & Meland, K. (2009) Lophogastrida of the Gulf of Mexico. In: Felder, D.L. & Camp, D.K. (Eds.), Gulf of Mexico—origins, waters, and biota. Biodiversity 1. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas, pp. 923–928.
- Richter, S. (2003) The mouthparts of two lophogastrids, Chalaraspidum alatum and Pseudochalaraspidum hanseni (Lophogastrida, Peracarida, Malacostraca), including some remarks on the monophyly of the Lophogastrida. Journal of Natural History, 37 (23), 2773–2786. https://doi.org/10.1080/0022293021000007417
- San Vicente, C. (2010) Mysidaceans. In: Coll, M., Piroddi, C., Steenbeek, J., Kaschner, K., Ben Rais Lasram, F., Aguzzi, J., Ballesteros, E., Bianchi, C.N., Corbera, J., Dailianis, T., Danovaro, R., Estrada, M., Froglia, C., Galil, B.S., Gasol, J.M., Gertwagen, R., Gil, J., Guilhaumon, F., Kesner-Reyes, K., Kitsos, M.S., Koukouras, A., Lampadariou, N., Laxamana, E., López-Fé de la Cuadra, C.M., Lotze, H.K., Martin, D., Mouillot, D., Oro, D., Raicevich, S., Rius-Barile, J., Saiz-Salinas, J.I., San Vicente, C., Somot, S., Templado, J., Turon, X., Vafidis, D., Villanueva, R. & Voultsiadou, E. (Eds.), The Biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: Estimates, Patterns, and Threats. PLoS ONE, 5 (8), e11842, Supporting information 2nd file, pp. 247–275. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011842
- San Vicente, C. (2016) An annotated check-list of lophogastrids (Crustacea: Lophogastrida) from the seas of the Iberian Peninsula. Zootaxa, 4178 (4), 481‒502. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4178.4.2
- Sars, G.O. (1870) Nye Dybvandscrustaceer fra Lofoten. Forhandlinger i Videnskabs-Selskabet i Christiania 1869, 147–174. [1869]
- Sars, G.O. (1883) Preliminary notices on the Schizopoda of H.M.S. Challenger expedition I. Forhandlinger i Videnskabsselskabet i Christiania, 7, 1–43.
- Sars, G.O. (1885) Report on the Schizopoda collected by H.M.S. “Challenger” during the years 1873–1876. Report on the Scientific Results of the Voyage of H.M.S. Challenger During the Years 1873–76. Zoology, 13 (37), 1–228. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.10425
- Sars, M. (1857) Om 3 nye Norske Krebsdyr. In: Forhandlinger ved de Skandinaviske naturforskeres syvende møde I Christiania den 12–18 Juli 1856. C.C. Werner & Co., Christiania, pp. 160–175.
- Sawamoto, S. (2014) Current status of mysid taxonomy in Southeast Asia. Marine Research in Indonesia, 39 (1), 1‒14. https://doi.org/10.14203/mri.v39i1.80
- Sawamoto, S. & Fukuoka, K. (2005) Lists of mysid species and references for their identification in Southeast Asian waters. Bulletin of Institute Oceanic Research and Development of Tokai University, 26, 79–93.
- Taniguchi, A. (1974) Mysids and euphausids in the eastern Indian ocean with particular reference to invasion of species from the Banda Sea. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India, 16 (2), 349–357.
- Tattersall, W.M. (1951) A review of the Mysidacea of the United States National Museum. Smithsonian Institution, United States National Museum Bulletin, 201, 1–292. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.16843
- Tattersall, W.M. & Tattersall, O.S. (1951) The British Mysidacea. Ray Society, London, 460 pp.
- Udrescu, A. (1984) Transpecific evolution (family level) within Lophogastrida. A new family—Gnathophausiidae (Lophogastrida, Mysidacea). Travaux du Muséum National d’Histoire Naturelle “Grigore Antipa”, 25, 59–77.
- Willemoës-Suhm, R. (1873) Notes from the “Challenger” VII, by W. Thomsen. Nature, 8, 400–403. https://doi.org/10.1038/008400a0
- Willemoës-Suhm, R. (1875) On some Atlantic Crustacea from the ‘Challenger’ Expedition (communicated by W. Thomson). Transactions of the Linnean Society of London. Second Series. Zoology, 1 (1), 23–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1875.tb00433.x
- Wittmann, K.J. (2020a) Addenda to the Lophogastrida and Mysida of the “Valdivia” Expedition 1898–1899, with description of a new species of Longithorax Illig, 1906 and range extension in Echinomysis chuni Illig, 1905 (Crustacea, Malacostraca). Spixiana. Zeitschrift für Zoologie, 43 (1), 81–92.
- Wittmann, K.J. (2020b) Lophogastrida and Mysida (Crustacea) of the “DIVA-1” deep-sea expedition to the Angola Basin (SE-Atlantic). European Journal of Taxonomy, 628, 1–43. https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2020.628
- Wittmann, K.J. & Ariani, A.P. (2010) Lophogastrida & Mysida. Biologia Marina Mediterranea, 17 (1), 474–483.
- Wittmann, K.J., Ariani, A.P. & Lagardère, J. (2014) Orders Lophogastrida Boas, 1883 Stygiomysida Tchindonova, 1981 and Mysida Boas, 1883 (also known collectively as Mysidacea). In: von Vaupel Klein, J.C., Charmantier-Daures, M. & Schram, F.R. (Eds.), Treatise on Zoology—Anatomy, Taxonomy and Biology: The Crustacea. Crustacea 4B. Koninklijke Brill NV, Leiden, pp. 189–396. https://doi.org/10.1163/9789004264939_006
- Wittmann, K.J. & Riera, R. (2012) Check-list of lophogastrids (Crustacea, Peracarida) from the Canary Islands. Revista de la Academia Canaria de Ciencias, XXIV (3), 63–80.
- Wittmann, K.J. & Wirtz, P. (1998) A first inventory of the Mysid fauna (Crustacea: Mysidacea) in coastal waters of the Madeira and Canary Archipelagos. Boletim do Museu Municipal do Funchal (História Natural), 5, 511–533.
- Wood-Mason, J. & Alcock, A. (1891) Natural history notes from H.M. Indian Marine Survey steamer “Investigator”, Commander R.F. Hoskyn, R.N., commanding. No.21. Note on the results of the last season’s deep-sea dredging. Annals and Magazine of Natural History, 6 (7), 186–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222939109460596
- Yolanda, R., Ambarwati, R., Rahayu, D.A., Budijastuti, W., Fitrihidajati, H., Kuntjoro, S., Rachmadiarti, F. & Purnomo, T. (2023) An annotated checklist of the species of Lophogastrida and Mysida (Crustacea: Peracarida) from Thailand and its adjacent waters. Zootaxa, 5244 (3), 201–232. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5244.3.1