Abstract
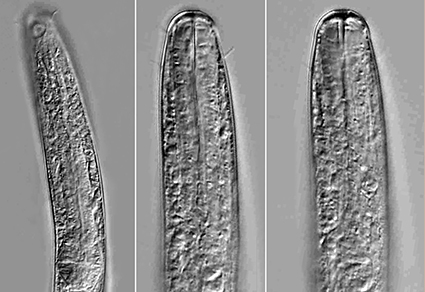
Two new free-living marine nematodes which were collected at silt beach of Rizhao along the Yellow Sea are identified here as Leptolaimus sinensis sp. nov. and Perspiria brevicaudata sp. nov. Leptolaimus sinensis sp. nov. is characterized by annulated cuticle with lateral alae, 2 µm in width; buccal cavity cylindrical; cephalic setae 2 µm long; amphidial fovea unispiral, circular in outline; six to seven evenly spaced tubular precloacal supplements and 23–29 continuous alveolar supplements extending from cloaca to level of the base of buccal cavity; spicules slender, slightly arcuate; gubernaculum with dorso-caudal apophysis; tail conico-cylindrical, about 6 times cloacal body diameter in males and elongated in females, about 9 times anal body diameter in length. Perspiria brevicaudata sp. nov. is characterized by having four cephalic setae and four cervical setae; small buccal cavity with dorsal tooth and minute ventral tooth; amphidial fovea unispiral, looking like double circle in outline, surrounded partially by cuticle striations; spicules arcuate with ventral velum, handle-like proximally and tapered distally; gubernaculum plate-shaped, without apophysis; twelve winged precloacal supplements present. Updated identification keys for group of Leptolaimus species characterized by the presence of both alveolar and tubular precloacal supplements and for species of Perspiria are also given.
References
Alekseev, V.M. & Rassadnikova, I.V. (1977) A new species and a taxonomic analysis of the genus Leptolaimus (Nematoda, Araeolaimida). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 56 (12), 1766–1774.
Allgén, C.A. (1947) Zur Kenntnis norwegischer Nematoden XI. Weitere Nematoden von der Insel Storfosen. Det Kongelige Norske Videnskabers Selskabs Forhandlinger, 19, 56–59.
Bütschli, O. (1874) Zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden, insbesondere der des Kieler Hafens. Abhandlungen der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft, IX, 1–56.
Castro, F.J.V., Bezerra, T.N.C., Silva, M.C. & Fonsêca-Genevois, V. (2006) Spirinia elongata sp. nov. (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from Pina Basin, Pernambuco, Brazil. Zootaxa, 1121 (1), 53–68.https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.1121.1.2
Chitwood, B.G. (1936) Some marine nematodes from North Carolina. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 3 (1), 1–16.
Cobb, N.A. (1914) Antarctic marine free-living nematodes of the Shackleton expedition. Contributions to a Science of Nematology, 1, 1–33.
Coles, J.W. (1987) Observations on the marine nematode genus Spirinia Gerlach, 1963 (Desmodoridae: Spiriniinae) with descriptions of two new species. Bulletin of the British Museum of Natural History, Zoology, 53 (2), 79–101.
Da Silva, M.C., Castro, F.J.V., Cavalcanti, M. F. & Da Fonsêca-Genevois, V. (2009) Spirinia lara sp. n. and Spirinia sophia sp. n. (Nematoda, Desmodoridae) from the Brazilian continental margin (Campos Basin, Rio de Janeiro). Zootaxa, 2081 (1), 31–45.https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.2081.1.2
De Coninck, L.A. (1965) Classe des Nématodes - Systématique des Nématodes et sous-classe des Adenophorea. Traité de Zoologie, 4 (2), 586–681.
de Jonge, V.N. & Bouwman, L.A. (1977) A simple density separation technique for quantitative isolation of meiobenthos using the colloidal silica Ludox-TM. Marine Biology, 42 (1), 143–148.https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391564
de Man, J.G. (1876) Onderzoekingen over vrij in de aarde levende Nematoden. Tijdschrift der Nederlandsche dierkundige Vereeniging, 2, 78–196.
Fadeeva, N.P. & Mordukhovich, V.V. (2007) New and known Leptolaimidae (Nematoda, Chromadoria) species in the Sea of Okhotsk and the Sea of Japan. Zoologicheskii Zhurnal, 86, 3–15.
Filipjev, I.N. (1922) Svobodnozhivushchiya Morskiya Nematody Okrestnostei Sevastopolya. I Vypusk. Russian Academy of Sciences, Petrograd, 611 pp.
Gadea, E. (1973) Sobre la filogenia interna de los Nematodos. Instituto de Biologia Aplicada, 54, 87–92.
Gagarin, V.G. & Nguyen, Vu Thanh. (2009) Two species of free-living nematodes of the family Leptolaimidae (Nematoda, Plectida) from mangrove of Mekong River Delta, Vietnam. International Journal of Nematology, 19 (1), 1–6.
Geng, C.X., Hao, Y.D. & Huang Y. (2021) Description of Leptolaimus boucheri sp. nov. (Nematoda, Leptolaimidae) from the Bohai Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 55, 2951–2960. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2022.2033868
Gerlach, S.A. (1963) Freilebende Meeresnematoden von den Malediven II. Kieler Meeresforsch, 19, 67–103.
Gharahkhani, A., Pourjam, E., Holovachov, O. & Pedram, M. (2020) Phylogenetic relationships of Leptolaimus de Man, 1876 (Plectida: Leptolaimidae) with description of two new species from the Persian Gulf, Iran. Nematology, 23 (2), 153–169.https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-bja10036
Holovachov, O. & Boström, S. (2013) Swedish Plectida (Nematoda). Part 4. The genus Leptolaimus de Man, 1876. Zootaxa, 3739 (1), 1–99. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3739.1.1
Holovachov, O. (2014) Order Plectida Gadea, 1973. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Eds.), Handbook of Zoology. Vol. 2. Nematoda. De Gruyter, Berlin, pp. 487–535.https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257.487
Huang, M., Sun, J. & Huang, Y. (2019) Daptonema parabreviseta sp. nov. (Xyalidae, Nematoda) from the Jiaozhou Bay of the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 37 (1), 273–277.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-7362-3
Huang, Y. & Wang, J. (2011) Two new free-living marine nematode species of Chromadoridae (Nematoda: Chromadorida) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 45, 2191–2201. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2011.591510
Huang, Y. & Zhang, Z. (2009) Two new species of Enoplida (Nematoda) from the Yellow Sea, China. Journal of Natural History, 43, 1083–1092.https://doi.org/10.1080/00222930902777945
Jensen, P. (1978) Four Nematoda Araeolaimida from the Öresund, Denmark, with remarks on the oesophageal structures in Aegialolaimus. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 19, 221–231.
Kito, K. & Aryuthaka, C. (1998) Free-living marine nematodes of shrimp culture ponds in Thailand. I. New species of the genera Diplolaimella and Thalassomonhystera (Monhysteridae) and Theristus (Xyalidae). Hydrobiologia, 379, 123–133.https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003489929579
Leduc, D. & Verschelde, D. (2015) New Spirinia and Stygodesmodora species (Nematoda, Spiriniinae) from the Southwest Pacific, and revision of the related genera Spirinia, Chromaspirina and Perspiria. European Journal of Taxonomy, 118, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.5852/ejt.2015.118
Leduc, D. (2020) Two new nematode species (Plectida: Leptolaimidae, Rhadinematidae) from Chatham Rise, New Zealand. PeerJ, 8, e9923.https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.9923
Leduc, D. (2021) New free-living nematode species and records (Chromadorea: Plectida and Desmodorida) from the edge and axis of Kermadec Trench, Southwest Pacific Ocean. PeerJ, 9, e12037. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12037
Lorenzen, S. (1972) Leptolaimus-Arten (freilebende Nematoden) aus der Nord- und Ostsee. Kieler Meeresforschungen, XXVIII (1), 92–97.
McIntyre, A.D. & Warwick, R.M. (1984) Meiofauna techniques. In: Holme, N.A. & McIntyre, A.D. (Eds.), Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp. 217–244.
Nemys (Eds.) (2022) Nemys: World Database of Nematodes. Available from: https://nemys.ugent.be (accessed 1 October 2022)https://doi.org/10.14284/366
Örley, L. (1880) Monographie der Anguilluliden. Termeszettudományi Fuzetek, 4, 1–165.
Pastor de Ward, C.T. (1984) Nematodes marinos de la Ria Deseado (Leptolaimina: Leptolaimidae, Haliplectidae) Santa Cruz, Argentina. Physis, Buenos Aires, Secc. A, 42 (103), 87–92.
Qiao, C.Y., Jia, S.S. & Huang, Y. (2020) Leptolaimus holovachovi sp. nov. (Nematoda) from Shenzhen mangrove nature reserve of Shenzhen City, China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 38, 1907–1913.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-019-9219-1
Sun, J., Zhai, H.X. & Huang, Y. (2019) Perspiria boucheri sp. nov. (Nematoda, Desmodorida) from the East China Sea. Zootaxa, 4695 (2), 195–200. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.4695.2.10
Tchesunov, A. (2014) Order Desmodorida De Coninck, 1965. In: Schmidt-Rhaesa, A. (Eds.), Handbook of Zoology. Vol. 2. Nematoda. Walter de Gruyter GmbH, Berlin/Boston, pp. 399–434.https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110274257.399
Tchesunov, A.V. (2015) Free-living nematode species (Nematoda) dwelling in hydrothermal sites of the North Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Helgoland Marine Research, 69 (4), 343–384.https://doi.org/10.1007/s10152-015-0443-6
Timm, R.W. (1962) Marine nematodes of the family Linhomoeidae from the Arabian Sea at Karachi. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 40, 165–178.https://doi.org/10.1139/z62-021
Vitiello, P. (1970 [1971]) Nématodes libres marins des vases profondes du Golfe du Lion. III. Monhysterida, Araeolaimida, Desmodorida. Téthys, 2, 647–690.
Vincx, M. & Gourbault, N. (1989) Desmodoridae from the Bay of Morlaix (Brittany) and the Southern Bight of the North Sea. Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 30, 103–114.
Wieser, W. (1954) Free-living marine nematodes II. Chromadoroidea. Lunds Universitets Arsskrift, Neue Folge 2, 50 (16), 1–148.
Wieser, W. & Hopper, B. (1967) Marine nematodes of the east coast of North America. I. Florida. Bulletin Museum of Comparative Zoology, 135, 239–344.