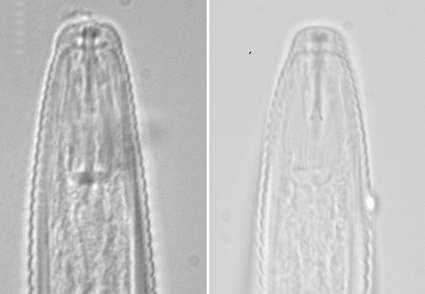
Abstract
To investigate relationships within the subfamily Telotylenchinae, more than 500 soil samples were collected from various natural and agricultural habitats in several localities of Iran. Individuals of seven known species, including Bitylenchus dubius, B. parvus, B. serranus, Sauertylenchus maximus, Tylenchorhynchus clarus, T. microconus and Trophurus ussuriensis, were recovered and characterized based on morphological and morphometric characters. Furthermore, phylogenetic relationships within representatives of the subfamily Telotylenchinae were explored using 13 sequences from the D2-D3 expansion regions of 28S ribosomal (r) DNA and 13 sequences for the partial 18S rDNA genes obtained in the present study. Analyses based on the relatively conserved 18S rDNA gene underlined the polyphyletic status of Tylenchorhynchus sensu lato, as three clusters representing Tylenchorhynchus, Bitylenchus and Sauertylenchus were well separated, and interspersed by, e.g., representatives of the Macrotrophurinae. Analysis of the more variable D2-D3 28S rDNA sequences suggested at least four clades within the subfamily Telotylenchinae: two clades dominated by Tylenchorhynchus species; a third clade harbouring representatives of Sauertylenchus, Bitylenchus, and Paratrophurus in distinct but unresolved branches;and a fourth clade dominated by Trophurus species. Although no molecular information was available from a number of genera that were originally gathered under Tylenchorhynchus sensu lato, we concluded that both Bitylenchus and Sauertylenchus should be seen as valid Telotylenchinae genera related to, but distinct from Tylenchorhynchus.
References
Allen, M.W. (1955) A review of the nematode genus Tylenchorhynchus. University of California Publications in Zoology, 61, 129–165.
Arias, M. (1970) Paratrophurus loofi n. gen., n. sp. (Tylenchidae) from Spain. Nematologica, 16, 47–50. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529270X00450
Baldwin, G., Luc, M. & Bell, A.H. (1983) Contribution to the study of the genus Pratylenchoides Winslow (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Revue de Nématologie, 6, 111–125.
Baqri, Q.H. & Jairajpuri, M.S. (1970) On the intra-specific variations of Tylenchorhynchus mashhoodi Siddiqi and Basir, 1959 and an amended key to species of Tylenchorhynchus Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda). Revista Brasilia Biologica, 30, 61–68.
Bert, W., Leliaert, F., Vierstraete, A.R., Vanfleteren, J.R. & Borgonei, G. (2008) Molecular phylogeny of the Tylenchina and evolution of the female gonoduct(Nematoda: Rhabditida). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 48, 728–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2008.04.011
Brzeski, M.W & Dolinski C.M. (1998) Compendium of the genus Tylenchorhynchus Cob, 1913 sensu lato (Nematodea: Belonolaimidae). Russian Journal of Nematology, 6 (2), 189–199.
Bütschli, O. (1873) Beiträge zur Kenntnis der freilebenden Nematoden. Nova acta Academiae Caesareae Leopoldino-Carolinae Germanicae Naturae Curiosorum, 36, 1–124.
Carta, L.K., Skantar, A.M. & Handoo, Z.A. (2010) Molecular rDNA phylogeny of Telotylenchidae siddiqi, 1960 and evaluation of tail termini. Journal of Nematology, 42, 359–369.
Castillo, P., Siddiqi, M.R. & Gomez-Barcina, A. (1989) Studies on the genus Paratrophurus Arias (Nematoda: Tylenchina) with descriptions of two new species. Nematologia Mediterranea, 17, 83–95.
Caveness, F.E. (1958) Clavaurotylenchus minnesotensis n.gen., n.sp. (Tylenchinae: Nematoda) from Minnesota. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 25, 122–124.
Caveness, F.E. (1959) Trophurus minnesotensis (Caveness, 1958) n.comb. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 26 (1), 64.
Chitwood, B.G. (1950) An outline classification of the nematodes.. In: Chitwood, B.G. & Chitwood, M.B. (Eds.), An Introduction to Nematology. I. Anatomy. Monumental Printing Co., Baltimore, USA, pp. 12–27.
Cobb, N.A. (1913) New nematode genera found inhabiting fresh water and non-brackish soils. Journal of the Washington Academy of Sciences, 3, 432–444. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.part.20323
De Grisse, A. (1969) Redescription ou modification de quelques techniques utilisées dans ľétude des nematodes phytoparasitaires. Mededelingen Rijksfaculteit Landbouwwetenschappen Gent, 34, 351–369.
De Waele, D. & Bolton, C. (1988) Trophurus pakendorfi n.sp. from sunflower in South Africa (Nematoda: Telotylenchinae). Phytophylactica, 20 (2), 153–155.
Decraemer, W. & Hunt, D.J. (2013) Structure and Classification. In: Perry, R.N. & Moens, M. (Eds.), Plant nematology. 2nd ed. Wallingford, Oxfordshire, UK, CAB International, pp. 3–32. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780641515.0003
Eroshenko, A.S. (1981) Plant parasitic nematodes of underwood; families Tylenchorhynchidae and Hoplolaimidae (Nematoda). In: Svobodnozhivuschie I fitopatogennye nematody fauny Dal'nego Vostoka Biol. Pedolog. Inst. of Far Eastern Research Center of USSR Academic Science Vladivostok, pp. 22–27 + 85–92.
Filipjev, I.N. (1934) Harmful and Useful Nematodes in Rural Economy. Moscow, Leningrad, USSR, 440 pp. [In Russian]
Filipjev, I.N. (1936) On the classification of the Tylenchinae. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 3, 80–82.
Fortuner, R. & Luc, M. (1987) A reappraisal of Tylenchina (Nemata). 6. The family Belonolaimidae Whitehead, 1960. Revue de Nématologie, 10, 183–202.
Ganguly, S. & Khan, E. (1983) Trophurus impar sp.n. and Scutellonema eclipse sp.n. (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Indian Journal of Nematology, 13 (2), 230–234.
Geraert, E. (2011) The Dolichodoridae of the World, Identification of the Family Dolichodoridae. Academia Press, Ghent, Belgium, 520 pp.
Ghaderi, R. & Karegar, A. (2018) Nematodes of the families Merliniidae and Telotylenchidae. In: Ghaderi, R., Kashi, L. & Karegar, A. (Eds.), Plant-parasitic nematodes in Iran. Marjaeelm Press & Iranian Society of Nematology, Shiraz, pp. 193–294. [In Persian]
Ghaderi, R., Karegar, A., Niknam, G. & Subbotin S. (2014) Phylogenetic relationships of Telotylenchidae Siddiqi, 1960 and Merliniidae Siddiqi, 1971 (Nematoda: Tylenchida) from Iran, as inferred from the analysis of the D2D3 expansion fragments of 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology, 16, 863–877. https://doi.org/10.1163/15685411-00002815
Gomez-Barcina, A., Siddiqi, M.R. & Castillo, P. (1992) The genus Bitylenchus Filipjev, 1934 (Nematoda: Tylenchida) with descriptions of two new species from Spain. Journal of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 59, 96–110.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, 41, 95–98.
Handoo, Z.A. (2000) A key and diagnostic compendium to the species of the genus Tylenchorhynchus Cobb, 1913 (Nematoda: Belonolaimidae). Journal of Nematology, 32, 20–34.
Handoo, Z.A., Palomares-Rius, J.E., Cantalapiedra-Navarrete, C., Liébanas, G., Subbotin, S.A. & Castillo, P. (2014) Integrative taxonomy of the stunt nematodes of the genera Bitylenchus and Tylenchorhynchus (Nematoda, Telotylenchidae) with description of two new species and a molecular phylogeny. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 172, 231–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/zoj.12175
Hodda, M (2022) Phylum Nematoda: a classification, catalogue and index of valid genera, with a census of valid species. Zootaxa, 5114 (1), 1–289. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5114.1.1
Holterman, M., Rybarczyk, K., Van Den Elsen, S., Van Megen, H., Mooyman, P., Pena-Santiago, R., Bongers, T., Bakker, J. & Helder, J. (2008) A ribosomal DNA-based framework for the detection and quantification of stress-sensitive nematode families in terrestrial habitats. Molecular Ecology Resources, 8, 23–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01963.x
Holterman, M., Karssen, G., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Bakker, J. & Helder, J. (2009) Small subunit rDNA-based phylogeny of the Tylenchida sheds light on relationships among some high-impact plant-parasitic nematodes and the evolution of plant feeding. Phytopathology, 99, 227–235. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-99-3-0227
Holterman, M., van der Wurff, A., van den Elsen, S., van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., Bakker, J. & Helder, J. (2006) Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23, 1792–1800. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl044
Hooper, D.J. (1978) The Tylenchorhynchidae. The identification of stunt nematodes Tylenchorhynchinae, Merliniinae and Trophurinae especially those in Western Europe. In: A manual prepared for the Workshop sponsored by the Nematology Group of the Association of Applied Biologists held at Rothamsted Experimental Station, Part II, 75 pp.
Hosseinvand, M., Eskandari, E., Ganjkhanloo, S., Ghaderi, R., Castillo, P. & Palomares-Rius, J.E. (2020) Taxonomical considerations and molecular phylogeny of the closely related genera Bitylenchus, Sauertylenchus and Tylenchorhynchus (Nematoda: Telotylenchinae), with one new and four known species from Iran. Journal of Helminthology, 94, e197, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X20000784
Jairajpuri, M.S. & Hunt, D.J. (1984) The taxonomy of Tylenchorhynchinae (Nematoda: Tylenchida) with longitudinal lines and ridges. Systematic Parasitology, 6, 261–268. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012204
Jairajpuri, M.S. (1982) Some studies on Tylenchorhynchinae: The subgenus Bitylenchus Filipjev, 1934, with description of Tylenchorhynchus (Bitylenchus) depressus n. sp. and a key to species of Bitylenchus. Mededelingen van de Fakulteit Landbouwwetenschappen Rijksuniversiteit Gent, 47, 765–770.
Jenkins, W.R. (1964) A rapid centrifugal-flotation technique for separating nematodes from soil. Plant Disease Reporter, 48, 692.
Khan, E. & Nanjappa, C.K. (1971) Trophurus similis sp.n. and Trichotylenchus astriatus sp.n. (Nematoda: Tylenchoidea) from Mysore, India. Indian Journal of Nematology 1 (1), 75–79.
Loof, P.A.A. (1956). Trophurus, a new tylenchid genus (Nematoda). Verslagen en Mededelingen Plantenziekundige Dienst, Jaarboek, 129 (1955), 191–195.
Loof, P.A.A. (1958) Some remarks on the status of the subfamily Dolichodorinae, with descriptions of Macrotrophurus arbusticola n.gen., n.sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchidae). Nematologica, 3, 301–307. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529258X00067
Loof, P.A.A. (1960) Miscellaneous notes on the genus Tylenchorhynchus (Tylenchinae: Nematoda). Nematologica, 4, (1959) 294–306. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529259X00507
Loof, P.A.A. (1963) A new species of Telotylenchus (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Nematologica, 9, 76–80. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529263X00151
Mahajan, R. (1974) Tylenchorhynchus kashmirensis sp.n. and Quinisulcius himalayae sp.n. (Nematoda:Tylenchorhynchinae) from India. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 41, 13–16.
Mavlyanov, O.M. (1978) [Two new species of Nematodes of the family Dolichodoridae (Nematoda: Tylenchida) from the root soil of cotton]. Parazitologiya, 12 (2), 138–142.
Minagawa, N. (1995) Bitylenchus iphilus sp.n. and Tylenchorhynchus kagasawai sp.n. (Nematoda: Tylenchida) from Japan. Afro-Asian Journal of Nematology, 5, 151–160.
Ronquist, F,. Teslenko, M., Van Der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Hohna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61, 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Saha, M., Chawla, M.L. & Khan, E. (1974) Trophurus lomus sp.n. (Tylenchida: Nematoda) from soil around roots of Prunus armeniaca from India. Indian Journal of Nematology, 3 (1973), 61–63.
Sher, S.A. (1974) Sauertylenchus labiodiscus n.gen., n.sp. from Australia (Nematoda: Tylenchorhynchinae). Journal of Nematology, 6, 37–40.
Siddiqi, M.R. & Basir, M.A. (1959) On some plant parasitic nematodes occurring in South India with description of two new species of the genus Tylenchorhynchus Cobb, 1913. Proceedings of the 46th Indian Science Congress Part IV (Abstracts), p. 35.
Siddiqi, M.R. & Siddiqui, Z.A. (1983) Paratrophurus acristylus sp. n. and Tylenchorhynchus graciliformis sp. n. (Nematoda: Tylenchida) from wheat fields in Libya. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 50, 301–304.
Siddiqi, M.R. (1960) Telotylenchus, a new nematode genus from North India (Tylenchida: Telotylenchinae n. subfam.). Nematologica, 5, 73–77. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529260X00424
Siddiqi, M.R. (1961) Studies on Tylenhorhynchus spp. (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Zeitschrift für Parasitenkunde, 21, 46–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260176
Siddiqi, M.R. (1970) On the plant-parasitic nematode genera Merlinius gen. n. and Tylenchorhynchus Cobb and the classification of the families Dolichodoridae and Belonolaimidae n. rank. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washingthon, 37, 68–77.
Siddiqi, M.R. (1971) On the plant-parasitic nematode genera Histotylenchus and Telotylenchoides gen. n. (Telotylenchinae), with observations on the genus Paratrophurus Arias (Trophurinae). Nematologica, 17, 190–200. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529271X00035
Siddiqi, M.R. (1973) Trophurus imperialis. C. I. H. Descriptions of plant-parasitic nematodes. Set 2, No. 22. Commonwealth Institute of Parasitology. Spottiswoode Ballantyne Printers Ltd. Great Britain.
Siddiqi, M.R. (1976) New plant nematode genera Plesiodorus (Dolichodorinae), Meiodorus (Meiodorinae subfam. n.), Amplimerlinius (Merliniinae) and Gracilancea (Tylodoridae grad. n.). Nematologica, 22, 390–416. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529276X00391
Siddiqi, M.R. (1986) Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects. Commonwealth Institute of Parasitology, Slough, UK, 645 pp.
Siddiqi, M.R. (2000) Tylenchida Parasites of Plants and Insects. 2nd edition. CABI Publishing, Wallingford, Oxon, UK, 833 p. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851992020.0000
Siddiqi, M.R., Mukherjee, B. & Dasgupta, M.K. (1982) Tylenchorhynchus microconus n. sp., T. crassicaudatus leviterminalis n. subsp. and T. coffeae Siddiqi and Basir, 1959 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Systematic Parasitology, 4, 257–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00009626
Steiner, G. (1937) Opuscula miscellanea Nematologica V. Tylenchorhynchus claytoni n.sp. an apparently rare nemic parasite of the tobacco plant. Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 4, 33–34.
Subbotin, S.A., Sturhan, D., Chizhov, V.N., Vovlas, N. & Baldwin, J.G. (2006) Phylogenetic analysis of Tylenchida Thorne, 1949 as inferred from D2 and D3 expansion fragments of the 28S rRNA gene sequences. Nematology, 8, 455–474. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854106778493420
Tarjan, A.C. (1973) A synopsis of the genera and species in the Tylenchorhynchinae (Tylenchoidea, Nematoda). Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington, 40, 123–144.
Thorne, G. & Malek, R.B. (1968) Nematodes of the Northern Great Plains Part I. Tylenchida [Nemata: Secernentea]. South Dakota University, Brookings, 111 pp.
Tobar Jiménez, A. (1969) Descripcion del Tylenchorhynchus ventrosignatus n.sp. (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Revista Iberica Parasitologia, 29, 349–403
Van Megen, H., van den Elsen, S., Holterman, M., Karssen, G., Mooyman, P., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., Bakker, J. & Helder, J. (2009) A phylogenetic tree of nematodes based on about 1200 full-length small subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Nematology, 11, 927–950. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854109X456862
Whitehead, A.G. & Hemming, J.R. (1965) A comparision of some quantitative methods of extracting vermiform nematodes from soil. Annals of Applied Biology, 55, 25–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-7348.1965.tb07864.x
Whitehead, A.G. (1960) Trichotylenchus falciformis n. g., n. sp. (Belonolaiminae n. subfam. : Tylenchida Thorne, 1949) an associate of grass roots (Hyparrhenia sp.) in Southern Tanganyika. Nematologica, 4 (1959), 279–285. https://doi.org/10.1163/187529259X00480
Yoder, M., Tandingan De Ley, I., King, I.W., Mundo-Ocampo, M., Mann, J., Blaxter, M., Poiras, L. & De Ley, P. (2006) DESS: a versatile solution for preserving morphology and extractable DNA of nematodes. Nematology, 8(3), 367–376. https://doi.org/10.1163/156854106778493448