Abstract
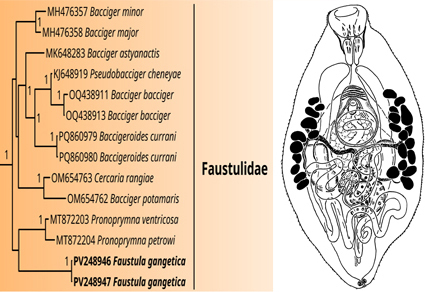
Faustulidae sensu lato is a polyphyletic assemblage of digeneans that parasitise marine or euryhaline fish as adults in the gastrointestinal tract. In previous phylogenetic reconstructions, this family appeared to be represented by two groups nested within the Gymnophalloidea and Microphalloidea. However, the choice of a correct name for these groups was impossible without assessing the phylogenetic position of the type genus of the Faustulidae, Faustula Poche, 1925. In the current study, we provide morphological and molecular data on Faustula gangetica (Srivastava, 1935), which represents the first molecular data for the genus Faustula. Specimens of F. gangetica were found in Tenualosa ilisha (Hamilton) from Shatt Al-Arab River, southern Iraq. We report the presence of discernible muscle fibres between the pharynx and the oral sucker, as well as a zone of distinctly differentiated transversely oriented muscle fibres located anterior to the common genital pore in this species for the first time. All molecular markers used in our study (ITS2 region, 28S rRNA gene) indicated that the genus Faustula is nested within the clade of gymnophalloid faustulids. Thus, Faustulidae sensu stricto is confirmed to belong to the Gymnophalloidea.
References
- Atopkin, D.M., Ivashko, Y.I., Izrailskaia, A.V., Tatonova, Y.V. & Besprozvannykh, V.V. (2024) Morphological and molecular data on Pseudozoogonoides ugui Shimazu, 1974 (Digenea: Microphalloidea: Zoogonidae) ex Pseudaspius hakonensis (Günther, 1877) and taxonomic problems in Zoogoninae genera. Journal of Helminthology, 98, e36. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X24000233
- Belousova, Y.V., Atopkin, D.M. & Vodiasova, E.A. (2023) The first modern morphological description of Cercaria pennata and molecular evidence of its synonymy with Pronoprymna ventricosa in the Black Sea. Journal of Helminthology, 97, e12. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X22000931
- Bodenhofer, U., Bonatesta, E., Horejš-Kainrath, C. & Hochreiter, S. (2015) msa: An R package for multiple sequence alignment. Bioinformatics, 31 (24), 3997–3999. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv494
- Bray, R.A. & Gibson, D.I. (1980) The Fellodistomidae (Digenea) of fishes from the northeast Atlantic. Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History), Zoology, 37 (4), 199–293.
- Bray, R.A. (1988) A discussion of the status of the subfamily Baccigerinae Yamaguti, 1958 (Digenea) and the constitution of the family Fellodistomidae Nicoll, 1909. Systematic Parasitology, 11 (2), 97–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012260
- Bray, R.A. (2008) Family Faustulidae Poche, 1926. In: Bray, R.A., Gibson, D.I. & Jones, A. (Eds.), Keys to the Trematoda. Vol. 3. CABI Publishing and the Natural History Museum, Wallingford, pp. 509–522. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851995885.0509
- Bray, R.A., Littlewood, D.T., Herniou, E.A., Williams, B. & Henderson, R.E. (1999) Digenean parasites of deep-sea teleosts: A review and case studies of intrageneric phylogenies. Parasitology, 119, 125–144. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000084687
- Calhoun, D.M., Curran, S.S., Pulis, E.E., Provaznik, J.M. & Franks, J.S. (2013) Hirudinella ventricosa (Pallas, 1774) Baird, 1853 represents a species complex based on ribosomal DNA. Systematic Parasitology, 86 (2), 197–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-013-9439-2
- Cardoso, D. & Cavalcante, Q. (2024) catGenes: a new R package for combining multiple DNA alignments for multigene analysis in phylogenetics and phylogenomics. Available from: https://github.com/domingoscardoso/catGenes (accessed 21 June 2025)
- Carpenter, K.E., Krupp, F., Jones, D.A. & Zajonz, U. (1997) The living marine resources of Kuwait, eastern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, 293 pp.
- Charif, D. & Lobry, J. (2007) SeqinR 1.0-2: a contributed package to the R project for statistical computing devoted to biological sequences retrieval and analysis. In: Bastolla, U., Porto, M., Roman, H. & Vendruscolo, M. (Eds.), Structural approaches to sequence evolution: Molecules, networks, populations, series Biological and Medical Physics, Biomedical Engineering. Springer Verlag, New York, New York, pp. 207–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-35306-5_10
- Cribb, T.H., Anderson, G.R., Adlard, R.D. & Bray, R.A. (1998) A DNA-based demonstration of a three-host life-cycle for the Bivesiculidae (Platyhelminthes: Digenea). International Journal for Parasitology, 28 (11), 1791–1795. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(98)00127-1
- Cribb, T.H., Miller, T.L., Bray, R.A. & Cutmore, S.C. (2014) The sexual adult of Cercaria praecox Walker, 1971 (Digenea: Fellodistomidae), with the proposal of Oceroma n. g. Systematic Parasitology, 88 (1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9478-3
- Curran, S.S., Warren, M.B. & Bullard, S.A. (2022) Description of a new species of Bacciger (Digenea: Gymnophalloidea) infecting the American Gizzard Shad, Dorosoma cepedianum (Lesueur, 1818), and molecular characterization of Cercaria rangiae. Comparative Parasitology, 89 (1), 9–29. https://doi.org/10.1654/COPA-D-21-00011
- Cutmore, S.C., Bray, R.A. & Cribb, T.H. (2018) Two new species of Bacciger Nicoll, 1914 (Trematoda: Faustulidae) in species of Herklotsichthys Whitley (Clupeidae) from Queensland waters. Systematic Parasitology, 95 (7), 645–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-018-9807-z
- Cutmore, S.C., Miller, T.L., Bray, R.A. & Cribb, T.H. (2014) A new species of Plectognathotrema Layman, 1930 (Trematoda: Zoogonidae) from an Australian monacanthid, with a molecular assessment of the phylogenetic position of the genus. Systematic Parasitology, 89 (3), 237–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9523-2
- De León, G.P.-P., Razo-Mendivil, U. & García-Magaña, L. (2012) Morphological and molecular evidences for the existence of two new species of Homalometron (Digenea: Apocreadiidae), parasites of cichlids (Osteichthyes: Cichlidae). Zootaxa, 3407 (1). https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.3407.1.3
- De Montaudouin, X., Bazairi, H., Mlik, K. & Gonzalez, P. (2014) Bacciger bacciger (Trematoda: Fellodistomidae) infection effects on wedge clam Donax trunculus condition. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 111 (3), 259–267. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao02769
- Diaz, P. (2018) Taxonomy, systematics and phylogenetic status of Faustulidae from corallivorous fishes in the Tropical Indo-west Pacific. PhD Thesis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Queensland, 117 pp.
- Dray, S. & Dufour, A.-B. (2007) The ade4 Package: implementing the duality diagram for ecologists. Journal of Statistical Software, 22 (4). [published online] https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v022.i04
- Dronen, N.O., Blend, C.K., Mohammed, E.T. & Bannai, M. (2021) Reconsideration of the species assigned to Faustula Poche, 1926 (Digenea: Microphalloidea) with the proposal of five new genera in the Faustulidae Poche, 1926. Zootaxa, 5027 (2), 231–253. https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5027.2.5
- Freyhof, J., Kaya, C. & Ali, A. (2021) A critical checklist of the inland fishes native to the Euphrates and Tigris drainages. In: Jawad, L.A. (Ed.), Tigris and Euphrates Rivers: Their Environment from Headwaters to Mouth. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 815–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57570-0_35
- Fricke, R., Eschmeyer, W.N. & Van der Laan, R. (2025) Eschmeyer's catalog of fishes: genera, species, references. Available from: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatmain.asp (accessed 11 June 2025)
- Garner, K.L., Mohammed, E.T., Blend, C.K., Bannai, M. & Dronen, N.O. (2019) Redescription of Faustula gangetica (Srivastava, 1935) (Plagiorchiida: Faustulidae) in the Hilsa Shad, Tenualosa ilisha (Hamilton) (Clupeidae), from the Arabian Gulf off Iraq. Comparative Parasitology, 86 (2), 89. https://doi.org/10.1654/1525-2647-86.2.89
- Georgieva, S., Faltýnková, A., Brown, R., Blasco-Costa, I., Soldánová, M., Sitko, J., Scholz, T. & Kostadinova, A. (2014) Echinostoma ‘revolutum’ (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) species complex revisited: species delimitation based on novel molecular and morphological data gathered in Europe. Parasites & Vectors, 7, 520. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-014-0520-8
- Gilardoni, C., Di Giorgio, G., Bagnato, E. & Cremonte, F. (2019) Survey of trematodes in intertidal snails from Patagonia, Argentina: new larval forms and diversity assessment. Journal of Helminthology, 93 (3), 342–351. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X18000329
- Hafeezullah, M. & Siddiqi, A.H. (1970) Digenetic trematodes of marine fishes of India. Part II. Fellodistomatidae. The Journal of Parasitology, 56 (5), 932. https://doi.org/10.2307/3277509
- Hall, K.A., Cribb, T.H. & Barker, S.C. (1999) V4 region of small subunit rDNA indicates polyphyly of the Fellodistomidae (Digenea) which is supported by morphology and life-cycle data. Systematic Parasitology, 43 (2), 81–92. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006113721899
- Holterman, M., Van Der Wurff, A., Van Den Elsen, S., Van Megen, H., Bongers, T., Holovachov, O., Bakker, J. & Helder, J. (2006) Phylum-wide analysis of SSU rDNA reveals deep phylogenetic relationships among nematodes and accelerated evolution toward crown clades. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 23 (9), 1792–1800. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl044
- Huber, W., Carey, J.V., Gentleman, R., Anders, S., Carlson, M., Carvalho, S.B., Bravo, C.H., Davis, S., Gatto, L., Girke, T., Gottardo, R., Hahne, F., Hansen, D.K., Irizarry, A.R., Lawrence, M., Love, I.M., MacDonald, J., Obenchain, V., Ole's, K.A., Pag'es, H., Reyes, A., Shannon, P., Smyth, K.G., Tenenbaum, D., Waldron, L. & Morgan, M. (2015) Orchestrating high-throughput genomic analysis with Bioconductor. Nature Methods, 12 (2), 115–121. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3252
- Le, C.T., Jeung, H.-D., Cho, Y.-G. & Choi, K.-S. (2024) Survey of trematodes in Manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum on the west coast of Korea: a preliminary study. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 206, 108172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jip.2024.108172
- Lockyer, A.E., Olson, P.D. & Littlewood, D.T.J. (2003) Utility of complete large and small subunit rRNA genes in resolving the phylogeny of the Neodermata (Platyhelminthes): Implications and a review of the cercomer theory. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 78 (2), 155–171. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1095-8312.2003.00141.x
- Mehra, H.R. (1963) Revision of Fellodistomoidea La Rue, 1957, families Fellodistomidae Woolcock, 1912, Gymnophallidae Dollfus, 1929 and Monodhelminthidae Dollfus, 1937. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of India, Biology Section, 32, 319–331.
- Morgan, J.A.T. & Blair, D. (1995) Nuclear rDNA ITS sequence variation in the trematode genus Echinostoma: an aid to establishing relationships within the 37-collar-spine group. Parasitology, 111 (5), 609–615. https://doi.org/10.1017/S003118200007709X
- Morgan, M. & Ramos, M. (2024) BiocManager: Access the Bioconductor Project Package Repository. R package version 1.30.25. Available from: https://bioconductor.github.io/BiocManager/ (accessed 21 June 2025)
- Nicoll, W. (1914) The trematode parasites of fishes from the English Channel. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom, 10 (3), 466–505. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315400008250
- Odhner, T. (1905) Die Trematoden des arktischen Gebietes. Fauna Arctica, 4, 289–372.
- Olson, P.D., Cribb, T.H., Tkach, V.V., Bray, R.A. & Littlewood, D.T.J. (2003) Phylogeny and classification of the Digenea (Platyhelminthes: Trematoda). International Journal for Parasitology, 33 (7), 733–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00049-3
- Pagès, H., Aboyoun, P., Gentleman, R. & DebRoy, S. (2024) Biostrings: Efficient manipulation of biological strings. R Package Version 2.74.0. Available from: https://bioconductor.org/packages/Biostrings (accessed 21 June 2025)
- Paradis, E. & Schliep, K. (2019) ape 5.0: An environment for modern phylogenetics and evolutionary analyses in R. Bioinformatics, 35 (3), 526–528. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty633
- Pérez-Ponce de León, G. & Hernández-Mena, D.I. (2019) Testing the higher-level phylogenetic classification of Digenea (Platyhelminthes, Trematoda) based on nuclear rDNA sequences before entering the age of the ‘next-generation’ Tree of Life. Journal of Helminthology, 93 (3), 260–276. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X19000191
- Pérez-Ponce de León, G., Anglade, T. & Randhawa, H.S. (2018) A new species of Steringotrema Odhner, 1911 (Trematoda: Fellodistomidae) from the New Zealand sole Peltorhamphus novaezeelandiae Günther off Kaka point in the Catlins, South Island, New Zealand. Systematic Parasitology, 95 (2–3), 213–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-018-9773-5
- Poche, F. (1925) Das System der Platodaria. Archiv für Naturgeschichte, 91, 1–458.
- R Core Team (2022) R: A Language and environment for statistical computing. R foundation for statistical computing. Available from: http://www.r-project.org/index.html (accessed 21 June 2025)
- Ramón, M., Gracenea, M. & González-Moreno, O. (1999) Bacciger bacciger (Trematoda, Fellodistomidae) infection in commercial clams Donax trunculus (Bivalvia, Donacidae) from the sandy beaches of the Western Mediterranean. Diseases of Aquatic Organism, 35, 37–46. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao035037
- Ronquist, F., Teslenko, M., Van Der Mark, P., Ayres, D.L., Darling, A., Höhna, S., Larget, B., Liu, L., Suchard, M.A. & Huelsenbeck, J.P. (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Systematic Biology, 61 (3), 539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
- Rudolphi, C.A. (1808) Entozoorum, sive vermium intestinalium historia naturalis. Vol. 1. Tabernae Librariae et Artium, Amstelaedami, 527 pp. [in Latin] https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.14422
- Rudolphi, C.A. (1819) Entozoorum synopsis cui accedunt mantissa duplex et indices locupletissimi. Augusti Rücker, Berlin, 811 pp. https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.9157
- Schliep, K.P. (2011) phangorn: Phylogenetic analysis in R. Bioinformatics, 27 (4), 592–593. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq706
- Simha, S.S. (1974) On a new species Faustula mandapamensis from the intestine of a marine fish, Stromateus cinereus, from India. Rivista di Parassitologia, 35, 99–102.
- Skrjabin, K.I. & Shul’ts, R.S. (1937) Trematody krupnugo rogatogo skota i ego moladnyaka. Sel’nozgiz, Moscow, 723 pp. [in Russian]
- Skrjabin, K.I. (1959) Order Faustulida (Poche, 1925) Skrjabin et Schulz, 1937. Family Faustulidae Poche, 1925. In: Skrjabin, K.I. (Ed.), Osnovy Trematodologii. Vol. 16. Izdatelstvo AN SSSR, Moscow, pp. 6–12.
- Snyder, S.D. & Tkach, V.V. (2001) Phylogenetic and biogeographical relationships among some holarctic frog lung flukes (Digenea: Haematoloechidae). Journal of Parasitology, 87 (6), 1433–1440. https://doi.org/10.1645/0022-3395(2001)087[1433:PABRAS]2.0.CO;2
- Sokolov, S., Gordeev, I. & Lebedeva, D. (2016) Redescription of Proctophantastes gillissi (Overstreet et Pritchard, 1977) (Trematoda: Zoogonidae) with discussion on the systematic position of the genus Proctophantastes Odhner, 1911. Acta Parasitologica, 61 (3). [published online] https://doi.org/10.1515/ap-2016-0070
- Sokolov, S.G., Shchenkov, S.V. & Gordeev, I.I. (2021) A phylogenetic assessment of Pronoprymna spp. (Digenea: Faustulidae) and Pacific and Antarctic representatives of the genus Steringophorus Odhner, 1905 (Digenea: Fellodistomidae), with description of a new species. Journal of Natural History, 55 (13–14), 867–887. https://doi.org/10.1080/00222933.2021.1923852
- Srivastava, H.D. (1935) New parasites of the genus Orientophorus, n. gen. (Family Fellodistomidae) from an Indian fresh-water fish, Clupea ilisha. Parasitology, 27 (3), 374–382. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182000015298
- Sun, D., Bray, R.A., Yong, R.Q.-Y., Cutmore, S.C. & Cribb, T.H. (2014) Pseudobacciger cheneyae n. sp. (Digenea: Gymnophalloidea) from Weber’s chromis (Chromis weberi Fowler & Bean) (Perciformes: Pomacentridae) at Lizard Island, Great Barrier Reef, Australia. Systematic Parasitology, 88 (2), 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11230-014-9494-3
- Tamura, K., Stecher, G. & Kumar, S. (2021) MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 38 (7), 3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
- Thaenkham, U., Nawa, Y., Blair, D. & Pakdee, W. (2011) Confirmation of the paraphyletic relationship between families Opisthorchiidae and Heterophyidae using small and large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Parasitology International, 60 (4), 521–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2011.07.015
- Tkach, V., Pawlowski, J. & Mariaux, J. (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of the suborder Plagiorchiata (Platyhelminthes, Digenea) based on partial lsrDNA. International Journal for Parasitology, 30 (1), 83–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(99)00163-0
- Tkach, V.V., Pawlowski, J., Mariaux, J. & Swiderski, Z. (2001) Molecular phylogeny of the suborder Plagiorchiata and its position in the system of Digenea. In: Interrelationships of the Platyhelminthes. 1st Edition. CRC Press, London, pp. 186–193.
- Truong, T.N. & Bullard, S.A. (2025) New Species of Baccigeroides (Digenea: Gymnophalloidea) Infecting Intestinal Mucosa of Gulf Menhaden, Brevoortia patronus Goode, 1878 (Clupeiformes: Alosidae) from the Northern Gulf of Mexico. The Journal of Parasitology, 111 (2), 132–142. https://doi.org/10.1645/24-142
- Wardle, W.J. (1983) Two new non-ocellate trichocercous cercariae (Digenea: Fellodistomidae) from estuarine bi-valved molluscs in Galveston Bay, Texas. Contributions in Marine Science, 26, 15–22.
- Wee, N.Q.-X., Cribb, T.H., Bray, R.A. & Cutmore, S.C. (2017) Two known and one new species of Proctoeces from Australian teleosts: Variable host-specificity for closely related species identified through multi-locus molecular data. Parasitology International, 66 (2), 16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.11.008
- Wickham, H., Hester, J. & Bryan, J. (2024) readr: Read Rectangular Text Data. R package version 2.1.5. Available from: https://readr.tidyverse.org (accessed 21 June 2025)
- Yamaguti, S. (1958) Systema Helminthum Vol. 1. The Digenetic Trematodes of Vertebrates. Interscience Publishers, New York, New York, 1571 pp.